How to save an image in Photoshop? Saving an image in JPEG format flexibly How to save in Photoshop
09.11.2018 09.11.2018
When the work in Photoshop is ready, it must be saved.
Depending on what task you are saving the file for, you need to choose a format. In this article, we will look at how to save and which file format to choose.
In what format should the file be saved?
PSD. This is the standard Photoshop file format. In it, you save your file so that you can continue working at any time. In PSD format, you won't be able to show your friends (parents, girlfriend, etc.) the photo or graphics you drew. This format can only be opened with Photoshop.
JPG. The format is great for photos and other graphic images. Before saving in Photoshop, you can optimize the saved JPG file- this means you can adjust the image quality so that the file size suits you. The format opens on any computers and phones. A good solution to show photos to relatives, send graphics to work, save a background for a website, etc.
PNG. It is mainly used by designers for graphics on websites, online advertising (banners), graphics for mobile applications etc. The format is notable for supporting transparency in the image. If you want to save an object to transparent background- save as PNG.
gif. This format is used if you want to save the animation. For example, an animated banner, emoticon, short video or sticker. Remember all the well-known GIFs that are walking around the Internet - this is just that format.
How to save to PSD
Give the file a name and select the PSD format (usually selected by default).
![]()
Be sure to check the checkbox Layers. Otherwise, everything will not be saved and there will be no benefit from such file saving.
How to save as JPG
- Execute the command File - Save.
- Choose format JPG.
![]()
After that, a window will appear where you can configure the parameters of the saved file.
![]()
Here you can adjust the quality of the photo by setting the value Quality from 1 to 12.
Check the checkbox of the preview option and you will see how the quality of the photo changes when you change the option Quality.
In addition, you can immediately see how much the file will weigh when you save it. The smaller the file, the faster you can send it over the Internet, the faster it will be loaded by another user. Remember that no one likes to wait a long time for uploading photos on the Internet, especially through a mobile phone.
![]()
A variation of the format is best left Progressive. Now we will not go into technical details, but this option is the best.
You need to adjust the quality when saving so that the image does not suffer much, while the file size is significantly reduced.
How to save as PNG
There is no need to save photos as PNG. Use this format if you need to save a high-quality image with a transparent background.
![]()
A window with settings for the saved image will appear.
![]()
Choose the PNG-24 format - this will be a high-quality image with the smallest file weight and with all colors.
Check the box Transparency so that the image has a transparent background.
Options - interlaced And Embedded Profile must be removed, because This is an extra and unnecessary load on the file.
How to save as GIF
Choose GIF format.
![]()
The GIF format seriously compresses the image in colors and, accordingly, in file weight. A maximum of 256 colors are available here.
Don't forget to check the box next to Transparency to have a transparent background if needed.
Adaptive the color model is the best when you want to save at maximum quality.
dithering I set it to 100%, in which case the gradient transitions are smoother.
![]()
If you have an animation in a GIF, then you can adjust its number of repetitions. Usually put many times to make the animation infinitely repeatable.
Now you know how to save in Photoshop using the most popular formats. Do you have any questions? I invite you to comment.
Today we will talk about how to properly save and optimize an image in Photoshop and in what format it is better to do it. But the correct choice of the save format greatly affects the quality and appearance images, as well as the weight of the image in kilobytes. This is especially important for those who take into account traffic consumption. So, let's deal with jpg, gif and png in order.
1. In what formats to save pictures
After you have opened your favorite photo in Photoshop and somehow conjured over it or, in general, created a collage of your own production from scratch, you have to save this file on your computer. There are three most common formats for saving a file.
jpg format. Perhaps the most common format. Suitable for saving complex graphics with many colors and shades and rich textures. That is, photos are best saved in this format. Among its disadvantages is that it does not support transparency and is very sensitive to red. 
gif format. In this format it is very good to save files with a limited number of colors. For example, text pages, tables, diagrams, logos, simple pictures. It turns out much clearer and weighs less. Plus, the format supports transparency and animation. However, the format is morally obsolete and is already inferior to the png format. 
png format. Similar to the previous format, but more advanced and more efficient in compressing pictures. In png, it is very convenient to save clipart on a transparent background. Exists in two png-8 formats (for simple pictures, supports 256 colors) and png-24 (for more complex images, supports colors well). 
2. Save using the "Save as ..." (Save as ...)
You can save the picture using the good old way through the menu "File" -\u003e "Save as ..." (Save as ...) or the key combination "Shift + Ctrl + S". In the drop-down menu, select the file format in which we want to save the file. (See the picture below) This method is used when the saved image will remain on your computer and is not intended for publication on the Internet. 
3. Save using the "Save for Web" (Save for Web ...)
If your picture is intended to be posted on the Internet, then it is better to use the "Save for Web" (Save for Web ...) function. With this method, the picture is better and better saved specifically for the Internet, and plus there are several convenient features. Select in the menu "File" -> "Save for Web ..." (Save for Web ...) or the key combination "Alt + Shift + Ctrl + S". A dialog box will open.
In order to save the image in jpg format, in the drop-down menu (1) select the JPEG format. We set the quality of preservation (2) from 75% to 95%. I always put 75%. Set, if necessary, the required dimensions of the image (3). The boxes on the left show the original image size (4) and the optimized image size (5). After that, click "Save". 
In order to save the picture in gif format, in the drop-down menu (1) select the GIF format. Select the number of colors to save (2). Set, if necessary, the required dimensions of the image (3). The boxes on the left show the original image size (4) and the optimized image size (5). After that, click "Save". 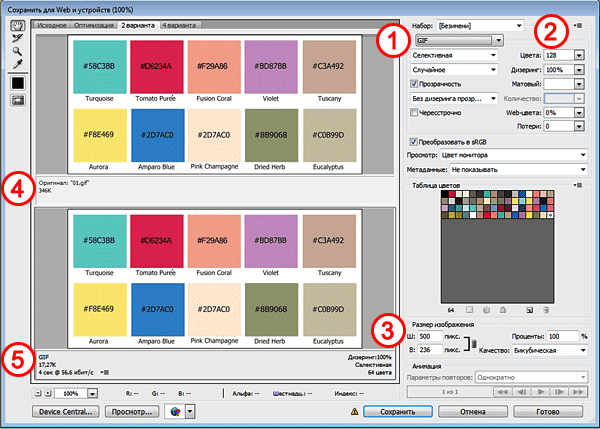
In order to save the image in png format, in the drop-down menu (1) select the PNG-8 format. Select the number of colors to save (2). Set, if necessary, the required dimensions of the image (3). The boxes on the left show the original image size (4) and the optimized image size (5). Put a tick in the checkbox "Transparency" (6) so that the background is transparent. After that, click "Save". 
If it is not immediately clear in which mode to save, it is best to try all the save modes, determining by eye the combination of image quality and its weight that is optimal for you after optimization. In general, it is useful to experiment with the settings in order to understand how a particular function works.
Preparation of any digital image readable graphic editor Adobe Photoshop, whether it's a PSD file, a TIF image, or a "large" JPEG image, for publication on a website, forum, or in social networks, as well as for shipment by e-mail. In other words, jpeg for the Internet. It worked out in rhyme.
Of course, the image formats that Photoshop can read are hardly limited to these three. And what's nice, most can be converted to JPEG. Regardless of the original format, there are two ways to "japegize" in Photoshop. The opportunity to choose is doubly pleasant. Both paths are different. External differences are revealed to the naked eye, differences in purpose (“Which way to follow?”) I will highlight specifically.
In this lesson, I will introduce two step by step instructions with the necessary theoretical "interspersed". It is designed to show you how best to save your virtual drawing, collage or photo in the widely used JPEG format. The latter is most effective for images with smooth color transitions.
To consolidate and expand the acquired knowledge, as well as to develop a skill, I have prepared the appropriate exercises. I suggest you complete them, and then publish your results in the comments to this lesson. Try out your skill in the "field conditions"!
First way
1 step
I open the original image in Photoshop. In my case, this is a file called "Example.psd" containing a drawn ball.
I press on the keyboard the combination of the keys "Ctrl", "Shift" and the key indicated Latin letter"S" or I select in the main menu "File" ("File")\u003e "Save As ..." ("Save As ..."). A dialog box titled "Save As" appears.
2 step

I choose the location of the future JPEG image. In the "File name" field, enter a new name for the image, if necessary. In the drop-down list "File type" I select the format "JPEG (*.JPG, *.JPEG, *.JPE)".
I leave the parameters below unchanged, making sure that the "standard" sRGB is specified and selected as the color profile embedded in the future JPEG image. If so, then go to the 4th step.
If another is specified instead of sRGB color profile, for example, ProPhotoRGB or AdobeRGB, before starting the procedure discussed in the lesson, I will convert the original image to the sRGB color space in order to display colors uniformly on most devices. I will do it in the following way.
3 step

I press the Esc key on the keyboard to close the Save As window.
I select in the main menu “Image” (“Image”)> “Mode” (“Mode”). If the “tick” is set opposite “8 bits\channel” (“8Bits\Channel”), then I select “16 bits\channel” (“16bits\Channel”). Increasing the color depth is desirable so that the conversion from one color profile to another goes smoothly. Visually, the change in color depth will hardly affect the original and final images.
Then I choose "Edit" > "Convert to Profile" from the main menu. A dialog box titled "Convert to Profile" appears.
In my case, the source color profile ("Source Space"), which describes the colors in the drawing, is called "Adobe RGB (1998)". I select the value "sRGB IEC61966-2.1" in the "Destination Space" drop-down list. I check the conversion parameters - they are located below: the parameter "Tool" ("Engine") is set to "Adobe (ACE)", "Method (rendering)" ("Intent") - "Relative Colorimetric" ("Relative Colorimetric"), set There is no check mark next to the “Use Black Point Compensation” option, there is no check mark next to the “Flatten Image to Preserve Appearance” option.
If you increased the color depth (I did this a little earlier), then the "Use Dither" option will be inactive. If there is only one layer in the open image (when you open JPEGs or "simple" TIFs, it usually is), then Flatten Image to Preserve View is also disabled.
I click the “Finish” (“OK”) button. The Convert to Profile window disappears.
4 step

A new dialog box titled "JPEG Options" appears in the main program window. The "Quality" parameter allows you to set the ratio of the quality of the output image and the volume that the image will occupy in the computer's memory. Thus, the payment for reducing the volume is the degradation of the quality of the original image. The lower the Quality setting, the smaller the size of the JPEG image.
In this example, I will stop at a value of 6.
To evaluate the quality of the image before saving, I will check the box next to the “Preview” parameter.
5 step

Set the value of the second parameter - "Format Options" - equal to "Standard optimized" ("Baseline Optimized"). The volume of the future JPEG image has decreased, but the image quality remains the same.
6 step

I click the OK button in the JPEG Options window and check the result.
I compare the volumes of the original PSD-drawing (~ 3000 Kb) and the final JPEG-picture (82 Kb). Thus, the JPEG file turned out to be about 36 times smaller than the original image with visually equal quality. Comfortable!
I draw your attention to the fact that the size of the final JPEG image remains the same, as in the original PSD image, it is 2480 pixels × 2480 pixels.
Second way
1 step

I open the original image in Photoshop.
I press the key combination "Ctrl", "Alt", "Shift" and the key marked with the Latin letter "S" on the keyboard, or select "File" > "Save for Web ..." in the main menu.
A new dialog box with the same title will appear.
2 step

3 step

I set the value of the parameter "Quality" ("Quality") to the maximum.
4 step

I reduce the size of the image using the "Image Size" parameter.
This is an optional operation, but it helps to significantly reduce the size of the future JPEG image, most often with minimal loss in quality. On the one hand, reducing the size will lead to a natural decrease in volume and, on the other hand, to a decrease in detail. The latter, in turn, limits my ability to print the final JPEG image. If I don't plan to print the latest one, then I'll forget about the restrictions.
In this example, I enter the value 600 in the “Width” field. The value in the “Height” field will automatically change. Also, the size of the output image will be automatically resized relative to the size of the original image, specified in the "Percent" field. Changes occur automatically and the "Percentage" field is in an active state if the fields-parameters "Width" and "Height" are connected, as evidenced by the corresponding icon located to the right of the named fields.
In the preview window on the left, I will evaluate the size and quality of the image. And I can find out the approximate volume of the latter by the number indicated, usually in kilobytes (Kb) or megabytes (Mb) under the left corner of the window.
5 step

I check the box next to the “Optimized” parameter.
6 step

If I want to further reduce the size of the output image, then I reduce the value of the “Quality” parameter (“Quality”). I recommend sticking to values in the range of 45-90.
In this case, I'll choose a value of 75.
As a result, the average, with an Internet access speed of one megabit (1 Mbits), the download time of my drawing from the Internet will be one second. It is indicated under the volume value of the future JPEG image.
At the same time, visually the picture turned out to be of quite acceptable quality, the tone transitions are quite smooth.
7 step

I check the box next to the “Convert to sRGB” option and select the “Monitor Color” value from the drop-down list below.
8 step

Finally, I check the box next to the "Embed Color Profile" option.
Actions on the 7th and 8th steps are desirable so that the future JPEG image is approximately the same displayed on various devices.
step 9

In the dialog box that appears with the title “Save Optimized As” (“Save Optimized As”), I select the location of the JPEG image and set its name, if necessary. I click the "Save" button in the active window. Both windows disappear. Now I can evaluate the result.
Close the original image. In the dialog box that appears asking you to save the changes, select "No" ("No").
The image obtained by the second method is convenient to use for publishing on the Internet. And the image obtained by the first method can be printed in addition to publishing on the Internet. In view of the fact that the size of the image did not change, it was not subjected to interpolation, which means that its quality is a priori higher than the quality of the image obtained by the second method.
I will tell you more about interpolation and its impact on the degradation of digital image quality in the lesson “What is interpolation?”

To consolidate the acquired knowledge, I suggest you not only save several of your own photos in JPEG format, but also complete the exercises attached to this lesson. The latter cover the challenges you may face in photography.
Instruction
A beginner should not delve too deeply into theory, but you should definitely know that JPEG is a format with a compression algorithm. A file of this format can have different extensions, for example? .jpeg, .jfif, .jpg, .JPG, or .JPE. It is very convenient in that it takes up much less space than a similar image in TIFF format or BMP. Unlike the latter, it has less image information. When viewing the original file on a monitor, this may not be too noticeable, but when the photo is printed in a laboratory or processed, the result may turn out to be of lower quality than the full information formats.
How you save a JPEG depends a lot on your goals. Before you save the picture, decide whether you will process, print on photo paper, or you just need to put the picture on a page on the Internet.
For post-processing or printing in a photo lab, save the image at the highest quality and size. When saving the desired image, open the menu File (File) and select Save as (Save as). Select the directory where the file will be saved. In the first line, enter the name, and in the second, select the JPEG format and click the Save button. If you did manipulations with the file, then a dialog box will pop up in front of you with a choice of the quality of the saved image. You should select the maximum quality with the slider or the corresponding number 12. Confirm your choice by pressing Ok. If you did not manipulate the image, then after saving it, the dialog box with the choice of JPEG quality will not open.
When saving a photo for publication on the Internet, modern resources themselves can change the size and quality of the downloaded JPEG. However, in some cases you have to do it yourself. Before saving the image, resize it by going to the Image menu and selecting Image size. Make sure the Constrain Proportions box is checked. Choose a unit of measurement that is convenient for you: centimeters, pixels, inches or millimeters, enter the required value of one of the sides in numbers and click Ok (in most cases, images from 800 to 1500 pixels on the largest side are used for web pages). Save the result, while choosing a lower quality. With its values from 8 to 10 and a small image size, visual differences from the original size are minimal, but the file size is significantly reduced.
Also in Adobe Photoshop there is a special module for optimizing and saving images for web pages, which may be more convenient. From the File menu, choose Save for Web. In the dialog box that opens, you will be presented with a preview window for the saved image and several options for settings. Select the 4-up or 2-up tab. The program will present you with four or two possible options optimized image. To save the right one, just click on the picture and click Save (Save). If the options do not quite suit you, then first use the tools located to the right of the image.
After completing all operations on the image (photo), it must be saved to your HDD, choosing a location, a format, and giving a name.
Today we will talk about how to save finished work in Photoshop.
The first thing you need to decide before starting the save procedure is the format.
There are only three common formats. This JPEG, PNG And gif.
Let's start with JPEG. This format is universal and suitable for saving any photos and images that do not have a transparent background.
A feature of the format is that during the subsequent opening and editing, so-called "JPEG Artifacts", the cause of which is the loss of a certain number of pixels of intermediate shades.
It follows that given format suitable for those images that will be used "as is", that is, they will not be edited by you anymore.
Unlike the previous format, PNG when re-editing (used in other works) does not lose quality (almost).
The last representative of the formats for today - gif. In terms of quality, this is the worst format, as it has a limited number of colors.
Let's get some practice.
To call the save function, go to the menu "File" and find the item "Save as" or use hot keys CTRL+SHIFT+S.


This is a universal procedure for all formats except gif.

Substrate
As we already know, the format JPEG does not support transparency, so when saving objects on a transparent background, Photoshop offers to replace the transparency with some color. The default is white.
Image Options
This is where the image quality is set.
Format variation
Basic (Standard) displays the image on the screen line by line, that is, in the usual way.
Basic optimized uses the Huffman algorithm for compression. I won’t explain what it is, look for yourself on the net, this does not apply to the lesson. I can only say that in our case this will slightly reduce the file size, which is not relevant today.
Progressive allows you to improve the quality of an image step by step as it is loaded on a web page.
In practice, the first and third varieties are most often used. If it is not entirely clear what all this kitchen is for, choose Basic ("standard").
Saving to PNG
When saving to this format, a window with settings is also displayed.

Compression
This setting allows you to significantly compress the final PNG file without quality loss. The screenshot shows compression.
In the pictures below you can see the degree of compression. The first screen is with a compressed image, the second is with an uncompressed one.


As you can see, the difference is significant, so it makes sense to check the box next to "Smallest/Slowest".
interlaced
Setting "Remove selection" allows you to show the file on the web page only after it is completely downloaded, and "Interlaced" outputs an image with gradual improvement in quality.
I use the settings as in the first screenshot.
Save to GIF
To save a file (animation) in the format gif needed on the menu "File" select item "Save for Web".

In the settings window that opens, you don’t have to change anything, as they are optimal. The only point - when saving the animation, you need to set the number of playback repetitions.

I hope that after studying this lesson, you have the most complete idea of saving images in Photoshop.