How to connect light music to an amplifier. Color music. Color music with RGB LED strip
Beginner Radio Amateur Competition
“My amateur radio design”
Competition design for a beginner radio amateur
“Five-channel LED color music”
Hello dear friends and site guests!
I present to your attention the third competition work (second competition of the site) of a novice radio amateur. Author of the design: Morozas Igor Anatolievich:
Five-channel LED color music
Hello radio amateurs!
Like many beginners, the main problem was where to start, what my first product would be. Started with what I wanted to purchase a home first. The first is color music, the second is high high quality amplifier for headphones. I started from the first one. Color music using thyristors seems to be a hackneyed option, so I decided to put together color music for LED RGB strips. I present you with my first job.
The color music scheme was taken from the Internet. Color music is simple, with 5 channels (one channel is white background). You can connect an LED strip to each channel, but for it to work at the input you need a low-power signal amplifier. The author suggests using an amplifier with computer speakers. I went from a complicated point, to assemble an amplifier circuit according to the datasheet on a TDA2005 2x10 W microcircuit. This power seems to me to be enough, even with a reserve. I diligently redraw all the diagrams in the sPLAN 7.0 program
Fig. 1 Color music circuit with an input signal amplifier.
In the color music circuit, all capacitors are electrolytic, with a voltage of 16-25v. Where it is necessary to observe polarity, there is a “+” sign; in other cases, changing the polarity does not affect the blinking of the LEDs. At least I didn't notice it. KT819 transistors can be replaced with KT815. Resistors with a power of 0.25 W.
In the amplifier circuit, the microcircuit must be placed on a radiator of at least 100 cm2. Electrolytic capacitors with voltage 16-25v. Film capacitors C8, C9, C12, voltage 63v. Resistors R6, R7 with a power of 1 W, the rest 0.25 W. Variable resistor R0 - double, with a resistance of 10-50 kohms.
I took a factory switching power supply with a power of 100W, 2x12v, 7A
On a day off, as expected, a trip to the radio market to purchase radio parts. Next task is to draw printed circuit board. For this I chose the Sprint-Layout 6.0 program. It is recommended by radio specialists for beginners. It is easy to study, I am convinced of this.

Fig 2. Color music board.

Fig 3. Power amplifier board.
The boards were manufactured using LUT technology. There is a lot of information about this technology on the Internet. I like it when it looks factory, so LUT did the parts too.

 Fig 3.4 Assembling radio components on a board
Fig 3.4 Assembling radio components on a board
 Fig 5. Checking functionality after assembly
Fig 5. Checking functionality after assembly
As always, the most “difficult” thing when assembling a radio circuit is to assemble everything into a housing. I bought the case ready-made at a radio store.

I made the front panel this way. I drew it in Photoshop appearance front panel where variable resistors, a switch and LEDs should be installed, one from each channel. Printed out the finished drawing inkjet printer on thin glossy photo paper.

I glue photo paper onto a degreased prepared panel with holes using wood glue:

Then I place the panels under the so-called press. For a day. As a press, I have a 15 kg barbell plate:

Final assembly:


Here's what happened:


Attachments to the article:
(2.9 MiB, 2,958 hits)
Dear friends and site guests!
Don’t forget to express your opinion on the competition entries and take part in voting for your favorite design on the site’s forum. Thank you.
Some suggestions for those who will repeat the design:
1. You can connect speakers to such a powerful stereo amplifier, then you get two devices in one - color music and a high-quality low-frequency amplifier.
2. Even if the polarity of connecting electrolytic capacitors in a color music circuit does not affect its operation, it is probably better to observe the polarity.
3. At the color music input, it is probably better to install an input node for summing signals from the left and right channels (). According to the author, judging by the diagram, the high-frequency color music channel (blue) is supplied with a signal from the right channel of the amplifier, and the remaining color music channels are supplied with a signal from the left channel of the amplifier, but it is probably better to supply a signal to all channels from the audio signal adder.
4. Replacing the KT819 transistor with KT815 implies a reduction in the number of possible LED connections.
Almost every novice radio amateur, and not only others, had a desire assemble a color music console or running fire to add variety to your music listening in the evening or at holidays. In this article we'll talk about a simple color music console assembled on LEDs, which even a novice radio amateur can assemble.
1. The operating principle of color music consoles.
Operation of color music consoles ( CMP, CMU or SDU) is based on frequency division of the spectrum sound signal with its subsequent transmission via separate channels low, average And high frequencies, where each channel controls its own light source, the brightness of which is determined by fluctuations in the sound signal. The end result of the console's operation is to obtain a color scheme that matches the piece of music being played.
To obtain a full gamut of colors and the maximum number of color shades, color music consoles use at least three colors:

The frequency spectrum of the audio signal is divided using LC- And RC filters, where each filter is tuned to its own relatively narrow frequency band and passes through only vibrations of this part of the audio range:
1
. Low pass filter(low-pass filter) transmits vibrations with a frequency of up to 300 Hz and the color of its light source is chosen red;
2
. Mid Pass Filter(PSC) transmits 250 – 2500 Hz and the color of its light source is chosen green or yellow;
3
. High pass filter(HPF) transmits from 2500 Hz and above, and the color of its light source is chosen blue.

There are no fundamental rules for choosing the bandwidth or color of the lamps, so each radio amateur can use colors based on the characteristics of his perception of color, and also change the number of channels and frequency bandwidth at his own discretion.
2. Schematic diagram of a color music console.
The figure below shows a diagram of a simple four-channel color music console, assembled on LEDs. The set-top box consists of an input signal amplifier, four channels and a power supply that supplies the set-top box with AC power.

Signal audio frequency supplied to contacts PC, OK And General connector X1, and through resistors R1 And R2 falls on variable resistor R3, which is a regulator of the input signal level. From the middle terminal of the variable resistor R3 sound signal through a capacitor C1 and resistor R4 arrives at the input preamp, assembled on transistors VT1 And VT2. The use of an amplifier made it possible to use the set-top box with almost any audio source.
From the output of the amplifier, the audio signal is supplied to the upper terminals of trimming resistors R7,R10, R14, R18, which are the load of the amplifier and perform the function of adjusting (tuning) the input signal separately for each channel, and also set the desired brightness of the channel LEDs. From the middle terminals of the trimming resistors, the audio signal is supplied to the inputs of four channels, each of which operates in its own audio range. Schematically, all channels are designed identically and differ only in RC filters.
Per channel higher R7.
The channel bandpass filter is formed by a capacitor C2 and passes only the high-frequency spectrum of the audio signal. Low and medium frequencies do not pass through the filter, since the capacitor resistance for these frequencies is high.
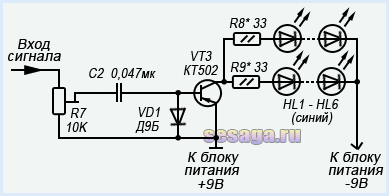
Passing the capacitor, the high-frequency signal is detected by a diode VD1 and is fed to the base of the transistor VT3. The negative voltage appearing at the base of the transistor opens it, and a group of blue LEDs HL1 — HL6 included in its collector circuit are ignited. And the greater the amplitude of the input signal, the stronger the transistor opens, the brighter the LEDs burn. To limit the maximum current through the LEDs, resistors are connected in series with them R8 And R9. If these resistors are missing, the LEDs may fail.
Per channel average frequency signal is supplied from the middle terminal of the resistor R10.
The channel bandpass filter is formed by a circuit С3R11С4, which for low and higher frequencies has significant resistance, therefore, to the base of the transistor VT4 Only mid-frequency oscillations are received. LEDs are included in the collector circuit of the transistor HL7 – HL12 Green colour.
Per channel low frequency signal is supplied from the middle terminal of the resistor R18.
The channel filter is formed by a circuit С6R19С7, which attenuates signals of medium and high frequencies and therefore to the base of the transistor VT6 Only low frequency vibrations are received. The channel load is LEDs HL19 – HL24 Red.
For a variety of colors, a channel has been added to the color music console yellow colors. The channel filter is formed by a circuit R15C5 and operates in a frequency range closer to low frequencies. The input signal to the filter comes from a resistor R14.
The color music console is powered by constant voltage 9V. The power supply unit of the set-top box consists of a transformer T1, diode bridge made on diodes VD5 – VD8, microcircuit voltage stabilizer DA1 type KREN5, resistor R22 and two oxide capacitors C8 And C9.
The alternating voltage rectified by the diode bridge is smoothed by an oxide capacitor C8 and goes to the voltage stabilizer KREN5. From the output 3 microcircuit, a stabilized voltage of 9V is supplied to the set-top box circuit.
To obtain an output voltage of 9V between the negative bus of the power supply and the output 2 chip included resistor R22. By changing the resistance value of this resistor, the desired output voltage is achieved at the pin 3 microcircuits.
3. Details.
The set-top box can use any fixed resistors with a power of 0.25 - 0.125 W. The figure below shows resistor values that use colored stripes to indicate the resistance value:

Variable resistor R3 and tuning resistors R7, R10, R14, R18 of any type, as long as they fit the size of the printed circuit board. In the author's version of the design, a domestic variable resistor of the SP3-4VM type and imported trimming resistors were used.

Permanent capacitors can be of any type, and are designed for an operating voltage of at least 16 V. If difficulties arise in purchasing a C7 capacitor with a capacity of 0.3 μF, it can be composed of two connected in parallel with a capacity of 0.22 μF and 0.1 μF.
Oxide capacitors C1 and C6 must have an operating voltage of at least 10 V, capacitor C9 not below 16 V, and capacitor C8 not below 25 V.

Oxide capacitors C1, C6, C8 and C9 have polarity, therefore, when mounting on a breadboard or printed circuit board, this must be taken into account: for Soviet-made capacitors, the positive terminal is indicated on the case; for modern domestic and imported capacitors, the negative terminal is indicated.

Diodes VD1 – VD4 any from the D9 series. A colored stripe is applied to the diode body on the anode side, identifying the letter of the diode.

As a rectifier assembled on diodes VD5 - VD8, a ready-made miniature diode bridge is used, designed for a voltage of 50V and a current of at least 200 mA.

If you use rectifier diodes instead of a ready-made bridge, you will have to slightly adjust the printed circuit board, or even move the diode bridge outside the main board of the set-top box and assemble it on a separate small board.
To assemble the bridge yourself, the diodes are taken with the same parameters as the factory bridge. Any rectifier diodes from the KD105, KD106, KD208, KD209, KD221, D229, KD204, KD205, 1N4001 - 1N4007 series are also suitable. If you use diodes from the KD209 or 1N4001 - 1N4007 series, then the bridge can be assembled directly from the printed circuit board directly on the contact pads of the board.
LEDs are standard with yellow, red, blue and green colors. Each channel uses 6 pieces:

Transistors VT1 and VT2 from the KT361 series with any letter index.

Transistors VT3, VT4, VT5, VT6 from the KT502 series with any letter index.

Voltage stabilizer type KREN5A with any letter index (imported analogue 7805). If you use nine-volt KREN8A or KREN8G (imported analogue 7809), then resistor R22 is not installed. Instead of a resistor, a jumper is installed on the board, which will connect the middle pin of the microcircuit to the negative bus, or this resistor is not provided at all during the manufacture of the board.

To connect the set-top box to the sound source, a three-pin jack connector is used. The cable is taken from a computer mouse.

Power transformer - ready-made or home-made with a power of at least 5 W with a voltage on the secondary winding of 12 - 15 V at a load current of 200 mA.
In addition to the article, watch the first part of the video, which shows the initial stage of assembling a color music console
This ends the first part.
If you are tempted make color music using LEDs, then select the parts and be sure to check the serviceability of diodes and transistors, for example. And we will carry out the final assembly and configuration of the color and music console.
Good luck!
Literature:
1. I. Andrianov “Attacks for radio receivers.”
2. Radio 1990 No. 8, B. Sergeev “Simple color and music consoles.”
3. Operating manual for the “Start” radio designer.
Below are circuit diagrams and articles on the topic “color music” on the radio electronics and radio hobby website.
What is “color music” and where is it applied, schematic diagrams of homemade devices that relate to the term “color music”.
I propose two simple CMU schemes. The first one was collected many years ago, was repeated by several radio amateurs and did not need any adjustment. The circuit is assembled using only six transistors of the KT315 type, they, of course, can be replaced with others... A simple, easily repeatable color-music installation using symmetrical thyristors and incandescent lighting lamps is described, which can be used to illuminate a hall or dance floor, because summer is coming! It has been said about color music... This music console has a relatively more power lighting lamps, namely: in each channel you can use lamps designed for a voltage of 220 V (one or more), or low-voltage lamps connected in 220 V garlands. Total power... Diagram of a simple color music set-top box for working with a tube radio, low-frequency amplifier or tape recorder. Contains a minimum of parts and is not difficult to assemble, a good option for beginner radio amateurs. Connect it to the secondary winding of the output transformer. For power supply... The color music circuit, the operating principle of the installation is based on dividing the spectrum of the sound signal by frequency. To achieve greater variety and richness of the color pattern, instead of the widespread three-color system, it uses a four-color system (red, yellow, blue and violet)... The color-music installation on thyristors develops a power of up to 2...3 kW at the load and can be recommended for color-music accompaniment of variety acts. In this case, it is advisable to mount powerful incandescent lamps in spotlights with color filters, directing them... Installation with pulse-number control of thyristors ensures proximity dynamic range lamp brightness and sound signal level, as well as obtaining light compensation channels without any special electronic devices. The power of each of the three main channels... Homemade color music using triacs, diagram and description of parts for self-production. Triacs are symmetrical thyristors that operate at any voltage polarity at the anode. They are used in household dimmers SRP-0.2-1. The installation is three-channel. The audio frequency signal is supplied to its input through step-up transformer T1, which also performs the functions... I would like to present to your attention a color music set-top box assembled on two synchronous binary counter-dividers (each counter is based on four D-flip-flops), also known as the K561IE10 microcircuit. This design is easily accessible for repetition, the K561IE10 microcircuit can still be bought at a radio store, and radio amateurs will probably have it in stock... The proposed simple devices are designed for creating lighting effects at discos and during various entertainment events. The signals they generate can control several lighting devices, switching them almost randomly Provided... The peak of popularity of color and music installations occurred in the 80s of the last century, now they have somehow almost been forgotten. And yet, time does not stand still, and there are new technologies that can revive “color music” in a new form. Here, for example, are three-color LED RGB strips or garlands... A diagram of a simple homemade three-channel color and music installation with a microphone for responding to sound in a room is given. The device “connects” to the equipment via acoustics, that is, there is a microphone at the input instead of a connector, and it perceives music directly in the room where it is... A three-color LED strip can be used as a screen for a color music installation. The advantage of RGB is LED strip is that it can be positioned as you like, either under a matte screen or, for example, hung like a garland on Christmas tree. Diagram of a color and music installation... This device is a typical analogue light and music set-top box, like those that were very popular in the 80-90s and are undeservedly forgotten today. The input signal is fed through a separate transformer to four active filters, dividing the signal into four... Circuit diagram homemade color music for three channels, it is based on LM567 tone decoders, S202S02 opto-keys are used for switching. The peak of popularity of color music installations occurred in the 80s of the last century. Now they have somehow almost been forgotten. And yet, time is not worth it... LED light and music circuit, simple design on K561IE16, K176IE4 microcircuits for beginner radio amateurs. In most cases, light and music installations are based on filters that divide the input audio signal into several bands. Then at the output of each of the strips there is a key... An interesting homemade device that changes the color of the LEDs according to the ratio of the frequency components of the audio signal. This device is not a full color music installation, because it works completely differently. The color music installation at the entrance has... Good afternoon, dear radio amateurs. This article appeared thanks to many questions devoted to ionophones of various types, sent to me after the publication of a series of articles on this topic. Especially often questions related to tube ionophones and their improvement and further development... Various options for light-dynamic installations (LDS) are widely presented in amateur radio literature. For the most part, they can be divided according to the principle of operation into two different groups: these are either garland (lantern) switches operating from a clock generator according to a specific program... Good afternoon, dear radio amateurs. Today I would like to continue a short series of articles devoted to ionophones, in response to numerous requests and questions that came after the publication of previous articles on this topic. The proposed version of the ionophone is, in fact, a more powerful version...Almost all color music devices of sufficient power are designed for the use of conventional incandescent lamps. There are also CMU circuits on LEDs on the Internet, but they are usually for low-power LEDs. How to connect 50-100 watt LEDs to such a device? You can take as a basis one very good color music scheme (also with sound control via a microphone) and slightly modify the output part - get the desired result.
CMU circuit for high-power LEDs
 Schematic diagram of the CMU for 220V
Schematic diagram of the CMU for 220V  Schematic diagram of the CMU for 12V
Schematic diagram of the CMU for 12V 


The electrical power supply for the input part of the frequency processing is made on a piece of a universal board. The transformer was taken from some kind of radio. It is ideal because it is symmetrical and has 10V windings. BT151/600 thyristors were used as powerful switches, with a margin so that they would not burn out from high currents.


The circuit can be made completely isolated from the network if the executive part is used using triacs and optocouplers.


When testing, temporarily install resistors of rated resistance and power from 10 W instead of LEDs.
CMU with 12 V LED strips
If you want to use 12 V LED strips in the CMU direct current, then you can power the entire circuit with the same 12 volts from a pulse network driver, and assemble the output part using powerful field-effect transistors.

A version of the diagram is shown above. Here resistor R2 sets the current limiting of the LED strip (or a powerful single LED).
By the way, when installing individual high-power LEDs, for example 100 watts (32 V at 3 A), supply the supply voltage from the driver through the LED to the drain field effect transistor(after making sure from the datasheet that it can withstand such U/I parameters), and set the above resistor to required level current


The body is made of wood (easier to find the material and easier to process). The holes for the lamps are drilled with large cutters. Naturally, on the front there are all the necessary knobs for adjusting signal levels and HF-MF-LF channels and a power button.
Do-it-yourself color music - what could be more pleasant and interesting for a radio amateur, because it is not difficult to assemble if you have a good circuit.
In modern radio engineering there is a huge variety of radio elements and LEDs, the advantages of which are difficult to doubt. Large range of colors, bright and rich light, high response speed various elements, low energy consumption. This list of advantages can be continued endlessly.
The principle of operation of color music: LEDs assembled according to the circuit blink from an existing sound source (this can be a player or a radio and speakers) at a certain frequency.
Advantages of using LEDs over those previously used in CMU:
- luminous saturation of light and a wide color range;
- good speed;
- low energy consumption.
The simplest schemes
A simple color music that can be assembled has one LED and is powered by a 6–12 V DC source.
You can assemble the above circuit using an LED strip and selecting the necessary transistor. The disadvantage is that there is a dependence of the LED blinking frequency on the sound level. In other words, the full effect can be observed only at one sound level. If you lower the volume, there will be a rare blinking, and if you increase the volume, a constant glow will remain.
This drawback can be eliminated using a three-channel sound converter. Below is a simple circuit; it is not difficult to assemble it with your own hands using transistors.
 Color music circuit with three-channel sound converter
Color music circuit with three-channel sound converter This circuit requires a 9-volt power supply, which will allow the LEDs in the channels to light. To assemble three amplification stages, you will need KT315 transistors (analogous to KT3102). Multi-colored LEDs are used as a load. A step-down transformer is used for amplification. Resistors perform the function of adjusting LED flashes. The circuit contains filters for passing frequencies.
The scheme can be improved. To do this, you need to add brightness with 12 V incandescent light bulbs. You will need control thyristors. The entire device must be powered from a transformer. According to this the simplest scheme You can already work. Color music using thyristors can be assembled even by a novice radio technician.

How to make color music using LEDs with your own hands? The first thing you need to do is select an electrical circuit.
Below is a diagram of a light and music system with an RGB strip. For such an installation, a 12 volt power supply is required. It can work in two modes: as a lamp and as a color music. The mode is selected by a switch installed on the board.

Manufacturing stages
It is necessary to make a printed circuit board. To do this, you need to take foil fiberglass with dimensions of 50 x 90 mm and a thickness of 0.5 mm. The board manufacturing process consists of several stages:
- preparation of foil PCB;
- drilling holes for parts;
- drawing paths;
- etching.

The board is ready, components have been purchased. Now begins the most crucial moment - the wiring of radio elements. The final result will depend on how carefully they are installed and sealed.

We assemble our printed circuit board with the components soldered on it into such an accessible lampshade.

Brief description of radioelements
Radioelements for electrical diagram They are quite affordable and it won’t be difficult to purchase them at your nearest electrical goods store.
For color and musical accompaniment, wirewound resistors with a power of 0.25–0.125 W are suitable. The amount of resistance can always be determined by the colored stripes on the body, knowing the order in which they are applied. Trimmer resistors can be both domestic and imported.
Capacitors produced by industry are divided into oxide and electrolytic. It won’t be difficult to select the ones you need by doing basic calculations. Some oxide capacitors may have a polarity that must be observed during installation.
You can take a ready-made diode bridge, but if you don’t have it, then a rectifier bridge can be easily assembled using diodes of the KD or 1N4007 series. LEDs are taken as usual, with a multi-colored glow. The use of LED RGB strips is a promising direction in radio electronics.
 LED RGB strip
LED RGB strip Possibility of assembling a color and music console for a car
If you manage to please with color music from an LED strip made by yourself, then a similar installation with a built-in radio can be made for a car. It is easy to assemble and quick to set up. It is proposed to place the set-top box in a plastic case, which can be purchased in the electrical and radio engineering department. The installation is reliably protected from moisture and dust. It is easy to install behind the car dashboard.
You can also make a similar case yourself using plexiglass.
The plates of the required dimensions are selected, two holes are made in the first part (for power supply), and all parts are sanded. We assemble everything using a heat gun.
An excellent lighting effect is achieved if you use multi-colored (RGB) tape.
Conclusion
The well-known saying “it is not the gods who burn the pots” remains relevant today. A diverse range of electronic components gives craftsmen wide scope for imagination. DIY color music on LEDs is one of the manifestations of limitless creativity.




