Kerio connect mail login to your personal account. What is Kerio Connect. Kerio Connect corporate email functionality
Lyrical digression. This article is of no use to any gurus and pros, well, they don’t work with kerio. I think it will be useful for beginners in system administration; step-by-step manuals are always in short supply. Well, I also wanted to show how to configure Kerio Mailserver as a full-fledged mail server, working through mx records, using users from Active Directory, connecting Outlook via MAPI, etc., because very often KMS is used as a simple POP3/SMTP server, when in fact it can easily compete with Exchange in small companies.
Task: install in the organization mail server on the base Kerio MailServer (KMS), ensure the receipt and sending of mail in the organization, employee access to mail inside and outside the organization.
What you need before installing the mail server:
- Availability of a registered domain name of the second (or at least third 🙂) level, in our case this is testcompany.ru.
- If you work through MX records, you will need access to edit these records. Usually a hoster or name registrar provides such a service.
- The actual server that meets the requirements: http://www.kerio.com/mailserver/requirements.
Installing Kerio MailServer
So we have an Active Directory domain, let's say testcompany.local, there is a domain controller dc01, there is a separate server for KMS, with installed Windows Server 2003 (or 2008), server name mail. If there is no domain, in principle everything will be similar, only a little simpler, since you will not need to configure a connection to AD.
We start the installation of Kerio MailServer, in the first steps Next, Next, etc. are everywhere. I usually choose English language(because the translation is lame, to be honest) and the installation type is Custom, but this is not necessary.
In the Administrative Account installation step, we specify the name of the mail server administrator account and, since it will be created in the local KMS database, I advise you to give it a name different from the name of the domain administrator, for example kmsadmin. This will allow the domain administrator to have normal, full-fledged mail. If the names match, this will not work.
The next step, (Email Domain) is very important, there we indicate the name of our email domain ( testcompany.ru):

At the Internet Hostname step, we indicate the external name of the mail server (the one that appears in mx records, see below), in our case mail.testcompany.ru(our server will be identified under this name when establishing SMTP sessions). You can then check this using the HELO/EHLO commands, for example.

Next, at the Store Directory installation step, we specify the path to the mail storage; it makes sense to place it on a separate physical disk/array to increase performance. If there are a lot of users and they work intensively with mail, then it is very desirable that this array be on SAS/SCSI disks.

As a result, when we log into the KMS > Configuration > Domains console, we get something similar to this:

That's it, the installation is complete, Kerio MailServer is ready to go. But there is one important point, about which I must warn you. In Configuration > SMTP Server > Relay Control tab the selector is selected by default Allow Relay only for and the checkbox is checked Users authenticated through SMTP server for outgoing mail. There is also another point Users from IP address group and there is a great desire to use it and allow relay from your local network. This should not be done, because if you check this box, then the presence or absence of a checkbox in the second item, Users authenticated through SMTP server for outgoing mail, will no longer have any meaning, oddly enough, apparently this is what the KMS developers intended. And after that, any unauthenticated client from your network (including viruses and network worms) will be able to send spam from your network without any problems and your server will very quickly be blacklisted. Therefore, I strongly advise not to check the box in the Users from IP address group item and leave the default settings:

It’s worth mentioning here that if you use clients on your local network that use the SMTP protocol to send mail, you will need to check the “SMTP server requires authentication” checkbox, otherwise they will not be able to send mail.
All settings in other items are quite functional by default and you should change them only if you are aware of what you are doing.
Creating Users
There are three ways to create users in Kerio MailServer:
- In the local Kerio MailServer database.
- Connect users from Active Directory (so-called mapping).
- Import users from Active Directory.
The first method is usually used if you do not have a domain, in which case you have no other options other than using a local (Internal) KMS database.
The second method is logical to use if you have a domain structure.
In the third method, accounts are imported from the Active Directory domain and users are created based on them in the local KMS database (as in the first option).
Creating users in the local Kerio MailServer database
To create a user when using a local database, you just need to go to the KMS console in Domain Setting > Users and add a user by clicking on the Add... > Create local user button.
The second method is more complicated; it requires setting up automatic mapping of users from AD.
Mapping users from Active Directory
To configure KMS to work with Active Directory users, you must first install Kerio Active Directory Extensions on the domain controller. If there are several controllers, then it is not necessary to install them on all of them, only on those to which Kerio MailServer will connect (in fact, in KMS you can only specify two at most). After installing them, go to the KMS > Configuration > Domains > Directory Service tab and enter the data we need there:

Hostname— the name of the domain controller (the one on which Kerio Active Directory Extensions were installed).
Username— domain user name to connect to the AD database (enough rights regular user, but... if you want to add users from the KMS console, you will have to add this account to the Account Operator group at a minimum). I recommend creating a special user for the connection (for example, kms_service) and checking the “Password never expires” and “User cannot change password” checkboxes so that at one point your connection to Active Directory does not fail.
Password— password of this user.
Secondary (backup) directory server — we register the backup domain controller here, if it exists, of course. Don't forget to install Kerio Active Directory Extensions on it too.
Active Directory Domain Name— at this point, check the box and write the name of the local domain, testcompany.local in our case, since our mail domain name is different from the Active Directory domain.
Click the Test Connection button and make sure everything is OK. If not, it means you entered something incorrectly, check everything again.
To check that everything is functioning normally, on the domain controller go to the Active Directory snap-in, select a user (created before installing KMS), right-click on it, select Kerio MailServer Tasks and create a mailbox:

We go back to KMS > Domain Setting > Users and make sure that our newly created user is present in the console.
In general, you should create a user immediately with a mailbox, but if it was not created immediately for some reason, you can create it either from Active Directory using Kerio MailServer Tasks, or if the kms_service account is included in the Account Operators or Domain Admins group in AD, then this can be done directly from the KMS console. KMS > Domain Setting > Users > Add… > Activate Active Directory user. Similarly, you can assign an email address to groups.
Practical advice: immediately create a distribution group that will include all users of the company; it is convenient to use for sending out any announcements to all employees of the company.
Importing users
If for some reason you need to import AD users into the local KMS database, then this is done in this way - go to KMS > Domain Setting > Users > Import button > Import from directore service:
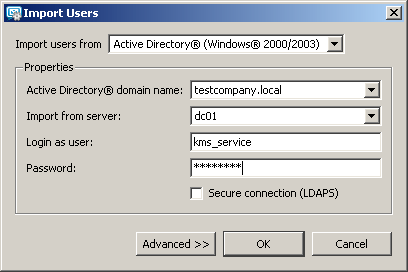
The name of the domain, controller, and user to connect to AD are the same as in the previous paragraph when mapping users from Active Directory. As a result, KMS prompts us to select users to import, select the ones we need and click OK:

That's it, users have been created. As a result, in KMS > Domain Setting > Users you get something like this:

e.popova and kmsadmin - users created in the local KMS database
i.petrov, p.ivanov and v.pupkin - users connected from Active Directory
n.sidorova - user imported from AD
Please note that the properties of users imported from AD are set to Kerberos 5 authentication by default, i.e. When a user logs into their mailbox, they are authenticated using AD. Naturally, you can change the authentication method to another - Internal or Windows NT domain (due to the fact that Windows NT is very outdated, this method is not discussed in this article). This cannot be done for users connected using the second method.
Setting up MX records
What are these records? An MX record is a special record on DNS servers, which for a given domain (testcompany.ru in our case) indicates the mail server to which email intended for addresses in this domain should be sent.
Access to editing these records is located where you actually purchased this name, most likely from the hoster or, say, from a name registrar, for example nic.ru.
Go to the control panel of the testcompany.ru zone. If you already had a company website there, for example, then you will see that there are already A-records there that point to the IP address of this site. We also need to create an A record that will point to our server. Actually, this record will be needed in order to use it in an MX record and so that it points to the web interface of our server.
Therefore, we introduce a new entry:
mail.testcompany.ru type A IP address 88.88.yyy.xxx
where 88.88.yyy.xxx is your external IP address given to you by your ISP. Often you don’t need to enter the entire mail.testcompany.ru, just mail is enough.
@ type MX mail.testcompany.ru. priority 10
@ means the domain testcompany.ru itself. Different name registrars enter these records slightly differently, but the meaning is this: for the testcompany.ru domain we create an mx record pointing to the mail.testcompany.ru A record. That's it, the records are created, after some time (up to two days, usually less) they are replicated to all DNS servers on the Internet and will be available. Therefore, it is advisable to do this point first, even though it comes fourth in my list.
We check using nslookup (how to use this command - http://support.microsoft.com/kb/200525/), it should be something like this:
C:\Documents and Settings\Admin>nslookup
Address: 192.168.1.10> set q=a
> mail.testcompany.ru
Address: 192.168.1.10Non-authoritative answer:
Name: mail.testcompany.ru
Address: 88.88.yyy.xxx> set q=mx
> testcompany.ru
Server: dc01.testcompany.local
Address: 192.168.1.10Non-authoritative answer:
testcompany.ru MX preference = 10, mail exchanger = mail.testcompany.rutestcompany.ru nameserver = ns2.zzz.ru
testcompany.ru nameserver = ns1.zzz.ru
mail.testcompany.ru internet address = 88.88.yyy.xxx
>
where 192.168.1.10 is the address of the domain controller dc01.
You will also need to create PTR record for your external IP address. It is needed to ensure that emails from your server are not considered spam (many mail servers have PTR checking). PTR records are usually created by a provider that provides you with a static IP address; there is usually no access to editing PTR records. Therefore, we write a letter to the provider with the following content:
Please create a PTR record for the address 88.88.yyy.xxx corresponding to the domain mail.testcompany.ru
You can check whether a record has been created or not, again via nslookup, something like this:
C:\Documents and Settings\Admin>nslookup
Default Server: dc01.testcompany.local
Address: 192.168.1.10> set q=ptr
> 88.88.yyy.xxx
Server: dc01.testcompany.local
Address: 192.168.1.10Non-authoritative answer:
xxx.yyy.88.88.in-addr.arpa name = mail.testcompany.ru
>
That's it, everything is fine with the records, now you need to map (or publish) SMTP and HTTP ports (as well as HTTPS, POP3, IMAP, etc., if you are going to give outside access to these services) on your corporate firewall. You also need to open the SMTP port to the outside from the mail server. For example, in Kerio Winroute Firewall it will look like this:
where 192.168.1.12 is the IP address of the mail server.
To quickly check outside, use telnet:
telnet mail.testcompany.ru 25
which should output:
220 mail.testcompany.ru Kerio MailServer 6.7.3 ESMTP ready
Client setup:
We check the web interface, on some workstation on the local network or on the server itself in the browser line we type the name of our mail server:
http://mail/ (or http://mail.testcompany.ru/ if you are trying outside)
We should get to the KMS web interface login page:

Then everything is standard, enter the username and password of the user with the existing mailbox, log in and are surprised that everything works :) You can also try logging in via HTTPS; by default, KMS itself creates a certificate during installation, so in this case everything should work.
First you need to install it on your workstation Kerio Outlook Connector (with offline caching). You can do this manually, or you can install the MSI package through group policies.
After installing Kerio Outlook Connector, launch Outlook, if there were no accounts, the wizard will start, if there were, you will need to start it manually from the menu Tools > Account Settings > Create...
On the Account Settings page, click Yes, of course, then on the page Automatic setup account, check the box “Manually configure server settings or additional server types” (since we don’t have Exchange :) Next on the Service Selection page Email select Other and Kerio Mailserver (KOC Offline Edition):

Server name - mail.testcompany.local
Account name - p.ivanov
Password - the password for this account in AD and check the Save password box.

Click the Detect button, the correct information about the user should be displayed. Next OK, OK, Done and go to Outlook. On this initial setup Outlook is finished, the user can send and receive mail.
To check, send several test letters within the organization and to some external addresses, as well as back :) If everything was done correctly, then the mail should function without problems.
Corrections and additions are accepted.
Today, many companies actively use email. And there is absolutely nothing surprising in this - this software allows you to quickly and cheaply exchange a wide variety of information. And therefore it is used both for internal corporate communication between company employees and for their communication with the “outside world”. However, truly effective use of e-mail in a company is impossible without organizing its own mail system.
Today, many companies actively use email. And there is absolutely nothing surprising about this - this service allows you to quickly and cheaply exchange a wide variety of information. And therefore it is used both for internal corporate communication between company employees and for their communication with the “outside world”. However, truly effective use of e-mail in a company is impossible without organizing its own mail system.
The key element of a corporate email system is mail server. This product provides all the necessary functionality for exchanging letters. Today there are many on the market mail servers. However, we recommend paying attention to, which recently released a new, now seventh, version. What's good about this product? On the one hand, it has a wealth of capabilities, and on the other, it is surprisingly easy to administer and use.
By the way, calling Kerio Connect mail server, frankly speaking, we sinned somewhat against the truth. The point is that - more than mail server. Today its functionality is much wider. It allows you to organize not only corporate postal system, but also provide general access company employees to the address book, calendars, task list, etc. That is, in fact, it can be considered a full-fledged replacement for Microsoft Exchange.
Setting up Kerio Connect
The basis of the product is mail server. And therefore, its configuration, for the most part, comes down to configuring the latter. Moreover, this process cannot be called particularly complicated. Any qualified system administrator can cope with it without any difficulties.
The configuration process begins with setting up services that are responsible for working with various protocols (SMTP, POP3, IMAP, NNTP, etc.). After this, a list of enterprise domains is entered. Moreover, for each you can set your own parameters and restrictions on the use of e-mail. In particular, you can set maximum size outgoing messages, enable automatic deletion of old letters, set up forwarding, set up a user authorization system, etc. Of particular note here is the possibility of the product in question as a distributed domain. What it is? A distributed domain, in essence, is a kind of cluster that unites several servers. At the same time, a unified information space is created that ensures collective work with data from all remote branches of the company, regardless of their geographical location.
The next step is to configure the SMTP server, which is responsible for sending letters. It has two operating modes. The first one is direct, when it sends messages independently, and the second one uses relaying. When using it, emails are transmitted through an external SMTP server. In addition, you can enable or disable user authentication, limit relaying, define the parameters of the queue into which messages are placed for sending, etc. After this, you need to set the Internet connection parameters. By default, it is assumed that the computer on which it is installed is permanently connected to global network. However, if necessary, the administrator can change these settings, in particular, specify the RAS service and its startup parameters.
At the end of the system configuration, you can set Extra options. For example, it is possible to enable the execution of certain actions on a schedule, specify external mailboxes from which correspondence will be downloaded and distributed among corporate accounts, etc. The system implements a large number additional settings, detailed description which can be found in the help system.
The final configuration step postal system is setting up a domain. This primarily includes user input. For each of them, you can set a list of mailboxes, set rules for forwarding incoming correspondence to various addresses, set administration rights, set quotas for the volume of the mailbox and the number of objects in it. Additionally, you can set rules for processing user messages. In particular, the administrator has the opportunity to allow sending and receiving mail only within his domain (to organize an internal mail system), limit the maximum size of outgoing messages, configure rules for deleting old messages, etc. For ease of configuration, all users can be divided into separate groups, each of which has its own parameters.
If necessary, you can create mailing lists. Moreover, each mailing can be very finely tuned. The administrator can set literally everything, starting with such “little things” as the text of the welcome message sent to a new subscriber, and ending with such serious issues as the rights to independently subscribe to the newsletter and send letters to it, assign moderators, etc.
Security in Kerio Connect
The term "security" in relation to mail server– a complex concept consisting of many different aspects. Firstly, it is protection against external threats: spam and viruses. Secondly, protection against mail server spoofing. Third, preventing insider activities. And finally, fourthly, protection against loss of messages stored in the database as a result of various failures. All these aspects are extremely important and should not be neglected under any circumstances. Fortunately, there are tools to protect against all of these threats.
To protect against spam, the product in question implements a universal multi-component filter. When enabled, all letters (except for messages sent from trusted addresses) undergo several checks, during which they are assigned digital assessment from 0 to 10. The higher it is, the more likely it is that the message being scanned is spam. What kind of checks do letters go through? First is the SpamAssassin filter, which is based on a trained Bayesian algorithm. Secondly, the system uses blacklists, not only user-defined ones, but also public databases of spammers’ IP addresses. Thirdly, a system of user rules is implemented. With its help, you can set a number of conditions (some of the fields of the letter are empty, non-empty, contain a certain substring, etc.), under which the message will be considered or, conversely, not considered spam. In addition, the administrator can enable and configure a number of additional security tools, such as sender ID authentication, SPF flag, and SMTP greeting delay.
To protect against viruses, the integrated Sophos subsystem is used. If, of course, when purchasing a license you chose the option with an integrated antivirus (it may be sold without it). In addition to it, the administrator can connect another of the anti-virus modules: Dr.Web, NOD32, etc. Naturally, for this it is necessary to purchase the appropriate product. In this case, checking of incoming correspondence can be carried out either by one subsystem or by two at once (alternately). Additionally, the administrator can activate an attachment filter, which allows you to block emails with certain types of files or delete attachments and only then deliver the email to the recipient.
Protection against mail server spoofing is provided by the ability to use secure communication protocols (secure POP3, SMTP, IMAP, etc.). Moreover, the ability to create, export and import the SSL certificates necessary for their operation is implemented.
The product in question also has an archiving and backup system. Despite their similar names, these two operations are fundamentally different from each other. Archiving ensures that correspondence is automatically saved with the ability to view it in the future. It can be used to protect against insiders. If suspicions arise or during the investigation of incidents, a manager or other responsible employee can view messages sent and received by certain users. A backup implies protection against information loss. This operation creates backup copies of the message store and the configuration of the entire system as a whole. As a result, if any failures occur, the administrator can quickly “reanimate” the mail system.
In addition, the product in question implements a number of additional security tools. Among them there are also quite original ones, but, of course, very useful features. So, for example, one cannot fail to note the function Kerio Smart Wipe. It allows you to delete mobile devices important information By wireless communication. This allows you to protect data from unauthorized access in the event of a smartphone being lost or stolen from an employee of the enterprise.
Using the mail system
In terms of use corporate mail cannot but surprise with its versatility. The fact is that with its help you can build a completely cross-platform system. Firstly, this server can work with a large number of clients for different operating systems: Windows, Linux, Mac. Secondly, it implements the function Kerio WebMail. It allows you to organize access to mailboxes via the web interface. It is especially convenient for remote access employees on business trips. The web interface allows them to use corporate email from anywhere in the world where there is Internet access.
Of course, one cannot help but mention that the product in question supports a large number of different smartphones running under Windows control Mobile, Symbian, Android, iOS and other mobile operating systems. This allows companies to organize mobile workplaces, the users of which can work with e-mail, receive information about new events in calendars, updates address books, tasks, etc.
Let's sum it up
Having considered the process of setting up and using the product, you can make sure that it functionality truly meet the requirements of the most demanding corporate users. In addition, it is easy to implement and use. Installing, configuring and maintaining a mail server does not require highly specialized skills. You can contact the partners of the 1Soft network.



All rights reserved. For questions regarding the use of this article, please contact
A full-fledged mail server with contacts, calendar, tasks, chat, protection against spam and viruses. Installs on any OS. GFI Web and Email Security">Web and Email Security 0
Description of Kerio Connect
Description of Kerio ConnectWhat is Kerio Connect

BYOD - bring your own device
Do your employees bring their devices into the workplace? Kerio Connect adds convenience to corporate communication and supports Cell phones based on iOS and Android out of the box

Support for any platform
Kerio Connect is more than just reliable email and flexible settings!
Kerio Connect Client, available for Windows and Mac and as a web app, allows employees to see colleagues who are online, write messages in real time, organize meetings and send emails securely.

Safe and secure email
Your mail is protected from hacking and attacks using SSL/TLS, S/MIME encryption, anti-spam filters, antiviruses and several layers of checks. Automatic backup with the ability to partially restore from backup copy allow you to quickly restore data even in the event of a critical failure.

Unrivaled simplicity
Kerio Connect is a complete solution for collaboration and messaging, easy to use and low cost. With MyKerio's centralized web interface, you can manage all your Kerio Connect devices from anywhere on the network, even from your tablet.
There is a special application to synchronize mail, contacts, and calendar - Kerio Connect Sync, but we will not install it for various reasons.
To work with email, we will configure an IMAP connection, which operating system Android supports natively.
IMAP configuration
To configure IMAP, follow these steps:
As an example, let's assume that your email address is master@site and your Kerio Connect server is located at mail.site
These values must be replaced own address email and the location of your Kerio Connect server.
1. From the Home screen, tap the Tools button, and then tap the Mail icon.
2.Enter your entire email address (for example, master@site), and in the second field enter the password associated with your account Email.

3. Click the "Default Settings" button and select "IMAP".
Username – Enter your email address (for example, master@site ). If there is one mail domain on the server, then only the name before the “@” icon is enough - master.
Password. Enter the password associated with your email account.
IMAP server – enter the name of the incoming mail server: mail.site
Port. Port number: 993
4. On the Outgoing Server Settings screen, enter the following information in the fields:
SMTP – server – enter the name of the outgoing mail server. We have the same server as for incoming: mail.site
Port. Port number: 465
Security Type – Select SSL/TLS (Accept all certificates)

Click the “Finish” button. All!
It should be noted that it will only work if the necessary ports are open on the firewall, in our case these are 993 and 465 tcp.
Setting up mail on Android to connect to Kerio Connect via IMAP.




