Graphic editor Paint. Paint program window. Set of tools. Drawing techniques. Pointer shapes and coordinates. Standard Windows programs: Graphic editor Paint in detail Free drawing tools
Graphics editor Paint is a Windows application designed for creating simple pictures. Children love to draw in Paint, and it becomes the first program for creating graphics, which begins a serious acquaintance with graphics programs.
Paint is included in the package of standard programs, so before turning your attention to expensive professional graphics programs, you should think carefully - the capabilities of this application may be sufficient. After all, it can be quite difficult for a person who is not involved in creating graphics on a daily basis to master these programs.
The interface of the Paint graphic editor is as simple as it is and the toolbar also consists of two tabs: “Home” and “View”. Also, the tools in the “Home” tab are intended for creating and editing objects, only they are needed here for creating drawings, not texts. The “View” tab is intended for displaying the picture and scaling it.
Under the toolbar there is a “canvas” for drawing, which can be stretched in different directions and compressed. Among the tools here there is a pencil, but using it does not bring much joy, since the lines do not turn out straight and even, because you have to draw with the mouse. Although some people may like this tool.
The Color Fill tool allows you to fill entire areas of a drawing that are bounded by lines with a selected color. You just need to select it, hover the cursor over the desired area and click on the left mouse button. And the area of the drawing we have chosen will immediately be filled with an even color. To use a particular tool, you need to click on its image on the toolbar with the left mouse button.
To insert an inscription into a drawing, there is the “Insert Text” tool, indicated by the capital letter A. After selecting this tool and specifying the area of the drawing where you want to insert the inscription, the additional “Text Input Tools” panel is automatically turned on. In which you can choose the type of font, its size and color, and whether letters are bold or italic. The ability to choose a transparent background for the inscription makes the drawings more beautiful.
The Tools, Eraser, and Magnifier perform the same functions as their real-life counterparts. But the “Palette” tool in the form of an eyedropper is designed to select the color of a picture or background. The color palette is also located in the “Home” tab. In this case, you can either select colors from those suggested by the palette or select new ones by clicking on “Change colors”. Here you can adjust the brightness of colors and shades.
The inability to draw a straight and even line on a sheet of paper does not mean that the same will happen in the Paint graphic editor, since any line or simple figure can be drawn by drawing a section of the figure. Squares, ovals, triangles, polygons, arrows and other shapes can be easily used to create simple drawings.
Another interesting tool is brushes, with which you can choose a brush, pen, spray paint, marker, pencil and more. Many people think that it is easier to draw not on a landscape sheet, but in an ordinary student notebook, lined with vertical and horizontal lines. And this can be done in Paint; the disabling “Ruler” and “Grid” tools, which are located in the “View” tab, will help here.
Thus, the Paint graphic editor, despite its simplicity and standardness, can help us create simple color pictures. And in many cases it replaces expensive and complex professional graphics programs.
Graphic editor Paint is included in standard programs operating system Windows. In terms of its capabilities, it is significantly inferior to professional graphic editors, but it has the necessary minimum tools for mastering the techniques of working with graphic information.
Appointment of the editor. The Paint program is simple editor raster graphics, which allows you to create black-and-white and color drawings and save them in files. Drawings can be printed, inserted into other documents, and used as a desktop background. The Paint editor can be used to view and edit photographs taken using a scanner and camera. Paint can be used to work with JPG, GIF, TIFF, PNG and BMP bitmaps.
Launch and program window. The graphic editor is launched with the command Start, Programs, Accessories, Paint.
After launch, the program’s working window opens on the screen, having a standard Windows application interface (Fig. 8.1).
The meaning of the commands on the program tape is as follows.
File. Contains commands for creating, opening, saving, closing, printing a document, etc.
Home. Commands for working with a selected fragment of a file, etc.
View. Commands for setting toolbars, palettes, scale.
Drawing. Commands for transforming a picture, setting its dimensions, setting background transparency.
Palette. Allows you to change the color palette.
The main part of the window is Workspace. The drawing can occupy part of the working area of the window or all of it, and even go beyond it. In the latter case, scroll bars appear at the edges of the work area. On the borders of the picture there are size change markers (dark dots in the middle of the sides and at the corners of the picture).
To the left of the work area toolbar contains drawing tool buttons. When you select a tool, a window for additional settings of its properties may appear at the bottom of the panel. When you slowly move the mouse pointer along the toolbar, a label with the name of the toolbar button appears.
Below the working area is located palette. It contains a set of colors that you can use when drawing. If the required color is not in the palette, you can create it and replace it with any of the colors in the palette.
Saving the drawing. As in others Windows applications, saving is performed with the command Paint, Save or Paint, Save As. Paint saves drawings in BMP format. Files of this format differ greatly
Rice. 8.1.
Small in size, but all Windows applications work with them. For web pages, Paint lets you save images in GIF, JPG, TIFF, and PNG formats, which produce smaller file sizes.
Drawing and graphic tools. The drawing is created using various tools. For the tool you click, select a color in the palette and, if necessary, adjust properties. There are main and background colors. The main color is used when working with tools, the background color is used as the color of the background canvas. All editor tools except Eraser, paint with the main color.
Eraser erases the image, replacing it with the background color (selected by right-clicking in the paint palette).
Line is intended for drawing straight lines when dragging the mouse. The line thickness is set in the settings. To make the line strictly vertical, horizontal or inclined at an angle of 45°, keep the key pressed while drawing Shift.
Pencil designed for drawing arbitrary lines. The thickness is set in the settings.
Curve used to create smooth curved lines. The thickness is selected in the settings. The construction is carried out in three steps: draw a straight line, then click and drag to the side of the line to set the first and second radii of curvature.
Brush used for free drawing of arbitrary curves, as well as for drawing using the padding method. First, select the brush shape in the settings palette, and then click the left mouse button to apply impressions to the drawing.
Spray used for free drawing and drawing using the typing method. The shape of the spot is selected in the settings.
Rectangle necessary for drawing rectangular shapes by dragging the mouse. If you hold down the key Shift, a square is being built. You can choose the method of filling the rectangle: no filling, filling with the foreground and background colors.
Rounded rectangle similar to a rectangle, but with rounded corners.
Polygon designed for drawing arbitrary polygons created by a series of drag-clicks. The closed shape can be automatically filled with paint according to the fill option selected in the setting.
Ellipse allows you to draw ellipses and circles (with the key pressed Shift).
Tool Selection forms a rectangular selection area, and Selecting a custom area – arbitrary. You can deal with the selected area as in all Windows applications: you can delete it, copy and cut it to the clipboard, and paste it from the clipboard. To reproduce repeating fragments, copy and paste the selected area. Two insertion modes: with or without preserving background graphics (background color dots in the pasted area are ignored). Switching the mode is done in the settings.
Operations with color. Tools for working with color Fill And Choice of colors, a color palette is used.
Fill serves to fill closed contours with the main or background color. Filling with the foreground color is performed by clicking the left mouse button, and filling with the background color is performed by clicking the right mouse button. If the contour is not closed, the tool does not work properly; in this case you should run the command Edit, Cancel.
Choice of colors allows you to select the main or additional color not from the paint palette, but directly from the drawing. This is important when you want to ensure color consistency across different areas of the image. After selecting the tool, point the pointer over the area of the picture with the desired color and click the mouse button. Clicking the left button sets the current color as the foreground color, and clicking the right button sets the current color as the background color.
Color palette contains a small selection of different colors to choose from, as well as a special window on the left with two overlaid squares. The top square corresponds foreground color, the bottom square defines background color. Paint allows you to use your choice of foreground and background colors in most operations. If the operation is performed using the left mouse button, the foreground color is applied. When you use the right button, the background color is applied. This applies to free-drawing, straight and curved line, and fill operations. Inst rument Eraser always fills the area being cleared with the background color. Standard geometric shapes are also filled with a background color. To select a color as a foreground color, left-click on it in the palette. Right-clicking selects this color as the background color.
If the required color is not in the palette, double-click on any color in the palette or give the command Palette, Change palette. Dialog window Changing the palette allows you to create any color.
In the command dialog Drawing, Attributes You can designate one color (for example, white) to be used as "transparent". Color transparency means that if a given image is displayed on top of another image (background), then the lower image will be visible through the upper one at those points that have a color designated “transparent”. The transparency property is saved in the picture file only when the .GIF graphic format is selected when saving. Drawings with transparent background widely used to create web pages and in electronic publications.
Scale of the drawing. To set the size of the picture, use the command View, Scale. This command opens a dialog box in which you can select the dimensions of the picture, set the units of measurement (pixels for preparing screen images, inches or centimeters for printed documents) and select a palette (black and white or color). To change the scale use the command View, Scale and tool Scale.
Work with text. Use the tool to enter text into a drawing. Text. Clicking on the picture opens a text entry field. The size of the input field is changed by dragging the input area markers - small rectangular nodes located on the sides and corners of the input area. Setting the font shape, its style and size is set using the text attributes panel by command Text, Text input tools. Small text should be avoided.
Image Transformation– automatic change of shape, location and size of graphic objects. Team Home, Flip/Rotate calls up a dialog box containing controls for symmetrically displaying a picture relative to the vertical or horizontal axis of symmetry, as well as for rotating it by a fixed angle, a multiple of 90°. Team Home, Stretch/Tilt Calls up a dialog box to stretch the drawing horizontally and vertically, tilt it relative to the horizontal or vertical axis. The stretch parameters are specified in percentages, and the tilt parameters are specified in angular degrees.
Team Home, Invert colors acts like a switch. The color of each pixel in the image changes to a color that is its complement to white.
Working with objects. To copy a fragment of a picture, select the fragment using the tools Selection And Selecting an arbitrary area. You can then copy or move the object by dragging it. If you hold down the key while dragging Ctrl, The object is copied. When a key is pressed Shift the dragged fragment leaves behind a “trace”, which allows you to create ornaments, borders and other effects.
In the window below the toolbar you can select object combination mode. It defines the behavior of the object's background color. In one case the background color is preserved, and in the other it is treated as "transparent". When constructing a picture from several objects, the second option is preferable.
To create a finished drawing using the montage method, it is convenient to open two Paint windows at once. The final drawing is created in one window, and the other is used to prepare objects to be superimposed on each other. After drawing the desired object in one window and selecting it, use the command Edit, Copy. Run the command in another window Edit, Paste. When you paste it into another picture, the object remains selected and you can drag it to the desired location.
Microsoft is one of the largest and most famous companies in the computer technology market and software. She is the creator of the internationally popular series of products Microsoft Office, actively used not only on computer devices, but also on smartphones. Now we'll talk about an equally well-known and relevant program - the raster graphics editor Paint.
What is this program?
Microsoft Paint is a fairly simple graphics editor. It is one of the mandatory programs. Comes with operating system Microsoft Windows. The Paint graphic editor is designed for creating and editing pictures of various colors and drawings. The works performed in this editor are called raster.
Under raster graphics refers to a collection of lines consisting of pixels. Their collection forms a two-dimensional array called a raster. It is worth noting that this editor there is one important disadvantage - poor scaling. This construction leads to the fact that when the file size is increased or decreased, the picture becomes distorted.
First version
The Paint graphic editor appeared in version 1.0 of the Windows operating system. After update 3.0 it began to be released under the name Paintbrush. After the release of Windows 95 and all subsequent ones, it acquired its standard name.

Starting with the Windows 98 operating system, the Paint graphics editor has the ability to save images in GIF and JPEG format. True, this could only be realized due to the presence of graphic filters on the computer, for example Office or PhotoDraw.
Updates on Windows 7
This version is almost the most popular among modern Microsoft systems Windows. At this particular stage, the Paint graphic editor has undergone significant changes. Among them we can highlight the updated library of shapes. In addition to the main ones present, such as ellipse, curve, vector, 17 completely new shapes have appeared. These included:
- Arrows in different directions.
- Stars with different numbers of ends.
- Isosceles and right triangles.
- Rhombus.
- Pentagon and hexagon.
- "Bubbles" for comics.
- Lightning.
- Heart and others.
The following 5 tools of the Paint graphic editor also appeared:
- 45 degree tilt for calligraphy brush to the right and left;
- oil and pastel brushes;
- marker;
- texture pencil;
- watercolor.
It is now possible to change the parameters of a drawn figure. The fill and outline tools have also undergone changes. The following options have appeared:
- Absence.
- Monochromatic.
- Pastel.
- Marker.
- Pencil.
- Watercolor.
- Oil.
Updates on Windows 10
New major updates to the Paint graphic editor have appeared here. Now the program has the ability to work with images in 3D format. Also in the Fall Creators Update old version editor was completely removed.

Menu of the standard graphic editor Paint
This panel is located at the top of the program. It contains the following items:
- File.
- Edit.
- Drawing.
- Palette.
- Reference.

File
Contains the following features:
- Create. When clicked, a blank sheet of standard size is created.
- Open. Click on this button and open the file available on your computer in the Paint graphic editor. When selected, a window will appear with the standard directory or the one that the program accessed last time. In the field that appears, you can select the destination folder yourself. When found required file Click on it with the left mouse button (hereinafter LMB, right mouse button) and click the “Open” button in the lower right corner. You can also double-click on the LMB file.
- Save. Saves the document under a standard name or instead of the previous file.
- Save as. Allows you to select the name and directory in which the document will be saved. When you select a function, a corresponding window will appear. In it you must enter the name of the saved file, the format of the saved image, and also select the folder in which it will be placed.
- Pave the desktop. Sets the maximum possible number of copies of the current picture (that will fit on the screen) as the desktop background.
- To the center of the desktop. Sets the current file as a desktop image, centered.

Edit
Contains the following commands:
- Cancel. An alternative to the Ctrl + Z keyboard shortcut. Undoes actions performed by the current tool.
- Cut out. Can be replaced with Ctrl + X. The selected section of the sheet will be cut and saved to the clipboard.
- Copy. It is also Ctrl + C. The selected fragment will be added to the clipboard.
- Insert. Alternative Ctrl + V. Pastes the element currently on the clipboard into the upper left corner of the project. Then it can be freely moved around the sheet.
- Clear selection. The specified fragment of the image will be deleted (can be returned with the “Cancel” command).
- Select all. Selects the entire project area.
- Copy to file... The selected fragment will be saved as a separate file.
View
This menu includes the following commands:
- Set of tools. Shows or hides the program toolbar;
- Palette. Shows or hides the palette.
- Status bar. Fixes it visible or removes the status bar.
- Text attributes panel. Shows or hides this feature.
- Scale. Allows you to resize the picture. There are three categories: regular, large (x4) and other. The latter allows you to change the zoom percentage from 100 to 800.
- View drawing. Places the drawing across the entire viewing area. When you click on any place in the picture, the LMB returns the previous state. Changing the pattern in this mode is impossible.

Drawing
Includes commands that can be used to change any selected worksheet element. This includes:
- Reflect. Mirrors the selected area of the sheet.
- To turn. Mirrors the entire project.
- Stretch. Allows you to stretch or shrink the project along the selected axis.
- Tilt. Tilts an object along the selected axis.
- Reverse colors. Changes the palette, displaying the opposite colors to those in the picture.
- Attributes. Change the size of the picture according to the specified units of measurement and the type of picture: black and white or color.
- Clear. Replaces the selection or the entire image with the background color.
- Opaque background. One of the colors is indicated as transparent. This means that the layer below will be visible through it. Moreover, it will be visible only in those places where there is a transparent color. This property can only be saved in gif format.
Palette
There is only one command here - change the palette. Allows you to create custom colors. To carry out this procedure, select the main color, call the specified function, after which the expanded color menu opens.

Tools
- for free drawing;
- for drawing lines;
- to create standard shapes;
- to fill areas with different colors;
- to highlight areas;
- before entering text.
Freehand Drawing Tools
- Pencil. A tool for freehand drawing of lines. The line thickness can be adjusted in the settings palette. To create a straight line, hold down the Shift key.
- Brush. Exactly the same as the previous one - used for drawing lines. The starting thickness of the pen is slightly wider.
- Spray. Creates a loose patch of pixels. Also used for free drawing.
- Eraser. Removes elements from an image, leaving the background color.
Line drawing tools
- Line. Used to create a straight line. The thickness is selected in the same place as other devices for free drawing. To create a tilt angle while drawing, hold down the Shift key.
- Curve. Allows you to create curved lines without sharp corners. The thickness is also selected in the settings palette. The construction occurs according to the following algorithm: the line itself is drawn, then the first and second bends are created using LMB to the side of the drawing.
Creating Standard Shapes
- Rectangle. Used to create the figure of the same name. Through the settings palette, you can choose how its internal space will be filled. It can be an empty frame, background or primary color.
- Rounded rectangle. Similar function. Only the shape of the corners of the figure has been changed.
- Polygon. Allows you to draw an object with an arbitrary number of angles.
- Ellipse. Performs the function of drawing ellipses or circles. The latter is created while holding down the Shift key.
Fill color
- Filling. Colors a closed area of a drawing with a background or foreground color. To use the main color, use LMB. For background – RMB. If the form is not closed, the entire project will be shaded.
- Selecting colors (aka eyedropper). The tool allows you to select a color not from the palette, but from the drawing itself. You need to move the cursor over the desired color and click LMB to set this color as the main color. RMB – as background.
Selecting areas
- Select a custom area. Using this tool allows you to select any necessary fragment. When the LMB is pressed, the required area is outlined. The ends must be connected. If the button was released before the form was closed, then the ends are closed along the shortest path. When you press LMB and RMB at the same time, the process will stop.
- Selection. Creates a rectangular area, allowing you to perform any manipulations with the selected fragment (paste into a picture or remove to the clipboard, drag). When moving with the Shift key pressed, a trace will be left.
Entering text
Includes the only function - the inscription. Performs text input function. After selecting the tool, a rectangular area is created. A text input field will be created in it. Next, by clicking inside the frame, we call up the attributes panel, which allows you to change the font and text size.
Results
Today, the graphic editor Paint is the most popular program for those who are not involved in professional design and drawing images on a computer. It is great for removing any unwanted components from an image, as well as for simple editing.
Using the Paint graphic editor, you can create simple black-and-white and color drawings or perform basic operations on processing finished images. Also, using this application you can easily convert graphic files from one format to another without resorting to special programs.
To launch the editor, you need to enter the “Start” menu by clicking on the corresponding button in the lower left corner of the screen, find the “Standard” folder and left-click on the Paint line in it.
The Paint editor is included in almost all modern and previous Windows versions. We will consider its edition included in Windows7 and it should be noted here that compared to Windows XP, appearance The editor has become somewhat different, although the functionality has remained virtually unchanged.

At the top of the program window on the left side there is a so-called panel quick access, which by default contains four elements: Save, Cancel, Return And .
![]()
The button with a floppy disk icon is designed to save the created (edited) image to a file. If you click on it, the current state of the image will be saved to a file.
If you were working on an image and for some reason the computer's power was turned off, all changes made since the last save will simply disappear. The fact is that, unlike other, more advanced editors, for example, programs included in Microsoft package Office and Paint do not have a document recovery feature. Therefore, while working, it is recommended to periodically click on the save button or use the Ctrl + S hotkey combination, which performs the same function, even if the drawing is not yet finished.
When saving for the first time, the editor will not yet know in which folder and under what name the drawing should be stored. Therefore, a standard window will open in which you must specify the folder to save the file, enter a name for the file in the “File name” field (the editor suggests the default name “Untitled”) and select the format in which it will be saved in the “File type” drop-down list image. Next, you need to click on the “Save” button.

When you subsequently save changes to the picture using this button, the specified window will no longer appear, since Paint already knows where to save the image.
To the right of the save button there are two icons with arrows, which are responsible for undoing and redoing completed actions. Like the vast majority of modern editors, Paint allows you to undo the last few manipulations. For example, you drew an image and added one element to it that looks completely unnecessary. What should I do? Why not redo everything again?
It is for such cases that the cancel action button is intended. Click on it with the mouse or use the keyboard shortcuts Ctrl + Z, and the last change you made will instantly disappear, as if it never happened. What if you were in a hurry and canceled in vain? last change? The redo button will help here. Click on it with the mouse, and the canceled changes will appear again. You can also use the hotkeys Ctrl + Y for this operation.
The last element in this area is the Quick Access Toolbar settings button. When you click on it, a drop-down menu will open in which you can specify which buttons you would like to see on this panel and which not, and select its location.

For example, you can remove all the above buttons by unchecking the boxes next to them, leaving only one Paint icon in the upper left corner. Or, conversely, add several other buttons (create, open, print, and so on). It is also possible to place the panel under the tape.
Below, under the panel quick launch there is a tape. Ribbon is a special strip containing tabs with buttons and various elements management.
At the top of the ribbon there are shortcuts for two tool tabs: home And View. By clicking on them you can switch from one tab to another. At first we see the tab elements home. But you can click on the name of another tab, that is, the tab View, and its elements will open before us. Then you can go back to the tab home by clicking on its name.

If necessary, the ribbon can be hidden to increase the area intended for working with the image. Paragraph Collapse the ribbon can be found in the pop-up menu that appears after clicking the button Customizing the Quick Access Toolbar.
Immediately below the ribbon there is a work area on which the image will be placed directly. Initially it looks like a white sheet. If the working area with the image does not completely fit in the editor window, then sliders appear to the right and below it, by moving which you can move the image in any direction horizontally or vertically.

Under the work area, at the very bottom of the program window, there is a status bar. The latter displays various auxiliary information, which is distributed over six areas.
In the first, leftmost area, we can see an image of a crosshair, next to which the location of the mouse cursor is indicated. It is shown in points measured from the upper left corner of the work area. The horizontal coordinates are specified first, and then the vertical ones. The image size is displayed next to the rectangle with arrows icon.
In the lower right corner of the Paint editor there is a scale that is used to change the scale of the working image. The current scale value is indicated to the left of this scale. Initially it is set to 100%. To change the scale, you can drag the slider to the right (increase) or to the left (decrease) or click on the round buttons - “plus” (increase) and “minus” (decrease). It should be borne in mind that by changing the scale, you do not change the size of the image, but only bring it closer or further away from you. Usually the scale is changed in order to examine or edit some small element of the picture.
Now, having become familiar with the main elements of the program window, let's get down to business and try to draw something. The tool is initially included Pencil. You can draw with it using your mouse the same way you would draw on a regular piece of paper with a real pencil. To create a line, you need to place the mouse cursor at a certain place in the Paint workspace, press the left mouse button and, without releasing it, drag the pointer over the place where the line should appear.
To select the line color, you need to go to the right side of the tab home in Group Colors Click the mouse to select the desired color square, after which the current color will immediately change.

If the colors in the provided palette do not suit you, you can click on the button in the same group Changing colors and in the window that opens Changing the palette choose a shade more precisely using the color panel on the right.

When finished selecting, click OK, after which the selected color will become the current color and will be added to the main group palette Colors .
In addition to the line color, you can also change its thickness. To make the line thicker, you need to click on the button Thickness and select one of the proposed samples from the list that opens.

In addition, we can set the method of drawing the line. To do this, click on the button Brushes and select a brush type from the list that opens.

From the images of the brushes you can see the principle of operation of each type. Of course, it’s best to check for yourself how this or that brush works, especially since we already know how to undo actions.
In the editor, you can not only manually draw lines, but also use ready-made shapes, a list of which will appear if you click on the button Figures in the group of the same name on the tab home. Let's look at the most commonly used shapes.

Line. Using this tool you can draw a straight line segment. To do this, you need to place the mouse cursor in the place where the line will begin and, pressing the left button, place it in the place where it should end, releasing the button. You can also change the line thickness. We already know how to do this. For more precise positioning of the line, you can use the Shift key. If you hold it down while drawing, you can create completely horizontal, vertical or inclined lines at an angle of 45 degrees. By holding down the right mouse button, you can create a line colored in the background color.
Curve. The tool is designed to create curved lines with smooth bends. Drawing is done as follows. First you need to create a straight line. Then, at the inflection point, press the left mouse button again and, without releasing it, move the cursor to the side, after which the straight line will turn into a curve passing from the starting point to the end point through the inflection point. Next, you can select another inflection point on the curve - it is created in the same way. As a result, we get a curve with two bends.
Rectangle. The tool allows you to create rectangular shapes with different outline thicknesses, as well as various sizes and colors. To draw a rectangle, you need to place the mouse pointer in the place where its upper left corner will be, press the mouse button and place the pointer where its lower right corner will be. To finish creating the rectangle, you need to release the mouse button. While holding down the Shift key, drawing a shape creates a square.
Polygon. The tool is used to create a sequence of straight lines in which the end of a segment coincides with the beginning of the next segment. This sequence creates the polygon.
Ellipse . The tool is designed to create circles of regular and irregular shapes (ellipses). The procedure for creating an ellipse is similar to creating a rectangle. While holding down the Shift key, drawing creates a circle.
Rounded rectangle. The tool allows you to create rectangles with rounded corners.
In the Paint editor we can draw other shapes, such as: triangle, right triangle, rhombus, pentagon, hexagon, right arrow, left arrow, five-pointed star, callout and so on.
Each figure, when drawn, takes on the appearance according to the selected outline and background coloring scheme, which is selected in the group Figures using buttons Circuit And Fill.

You can change these parameters both before and after you start drawing the figure.
In addition to filling shapes, in the Paint editor it is possible to fill any area of the canvas with the selected color. To perform this action, click on the button Fill color in Group Tools on the tab home.

This tool allows you to paint a closed area of a drawing with the line color (left mouse button) or the background color (right mouse button). If the boundaries are not closed, the neighboring areas up to the closed boundary will also be shaded. As we already know, if another area is unexpectedly painted, you can cancel the action, and by zooming in, find the gap and make the border closed.
Next useful tool in this group is Eraser, which allows you to hold down the left mouse button to erase objects that fall in the path of the mouse cursor, while painting the trace with the current background color. The width of the mark, as in the case of brushes, can be selected in the drop-down list Thickness. If you use the right mouse button when working with the eraser, it will replace the background color only with those colors that match the current line color.
In addition to various graphic objects, the drawing can be supplemented with text. The button with the letter “A” in the group is for this purpose. Tools. Having selected this tool, you need to click the mouse in the place on the canvas where the text should appear, after which a rectangular area will appear for entering it. At the same time, an additional tab will appear on the ribbon Text, in which you can select the font, size, color, style (bold, italic and underline) and other text attributes.

Having set the necessary parameters, click on the selected rectangular area and enter the text you need on the keyboard. While a frame with a selected area of text is open in front of you, you can make various changes to both the text itself and its attributes, for example, change its color or size. Clicking outside the selected area will make the text part of the drawing.
If you plan to finish drawing, but don’t remember what exact shade of color you drew, use the tool Palette, allowing you to select a color in any area of the image. To do this, left-click on the icon with a picture of a pipette, hover the mouse cursor over the element of the picture with the color of which you plan to draw further and click the left mouse button again.
In addition to providing the ability to draw, the Paint editor allows you to do some work on areas of the image. useful actions. To do this, you first need to select the required fragment. The editor has two tools that allow you to do this - a rectangular area and a free-form area (lasso).
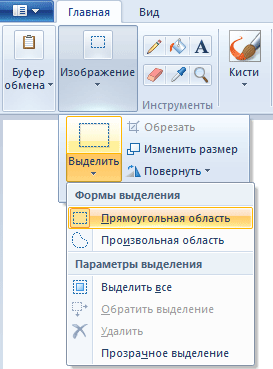
To select a rectangular area of the image, you must first select the appropriate tool by clicking on the ribbon tab home by button Image. Then select the section in the menu that opens Select, and then point Rectangular area. Next, you need to place the mouse cursor in the shape of a cross at the place where the upper left corner of the area we are selecting will be, press the left mouse button and, without releasing it, drag the cursor to the place where the lower right corner of the area will be, and then release the button. In this case, a dotted frame should appear, in the corners of which, as well as in the center of each side, there are small squares with which you can change the size of the selection.

While the area we created is active, it can be placed elsewhere in the image. In this case, in place of the removed fragment there will be an empty space painted over with the background color. If you move a fragment while holding down the Ctrl key, a copy of the fragment will appear.
You can perform other actions with this fragment, for example, you can place it in Clipboard- a special virtual “pocket” in Windows system, in which you can put part of a drawing or text for a while. This area of memory is common to all applications, so you can move something into it from one application and then retrieve it in another. For example, you can move a fragment of a picture that we drew in the Paint editor into the “pocket”, and take it out in text editor Microsoft Word and set as image to text.
To work with Clipboard there is a button with the same name located on the left side of the ribbon in the tab home.

Clicking on it opens a menu containing three commands:
- Cut. This operation moves the selected image fragment to the clipboard, leaving behind only empty space;
- Copy. This operation places the selected fragment on the clipboard, creating a copy of it;
- Insert. This operation returns from the clipboard the fragment of the picture we previously placed. It appears as if on top of the picture and after that, using the mouse, we move it to the desired place. The pasted fragment from the clipboard appears in the upper left corner of the editor's workspace and remains selected until we drag it to the desired location. Clicking outside a given fragment makes it inactive and leaves it in the drawing in its original place.
By the way, you can insert into an image not only a fragment stored in the clipboard, but also a picture from another file. For this, the Paste function has a menu item Paste from.
We already know how to select a fragment, move it around the work area and place it on the clipboard. But there are other actions that can be performed with it - for example, rotate it by a certain angle. To do this, click on the button Image on the tape. An item will appear in the menu that opens To turn. In the submenu you should choose exactly how to rotate the selected fragment.
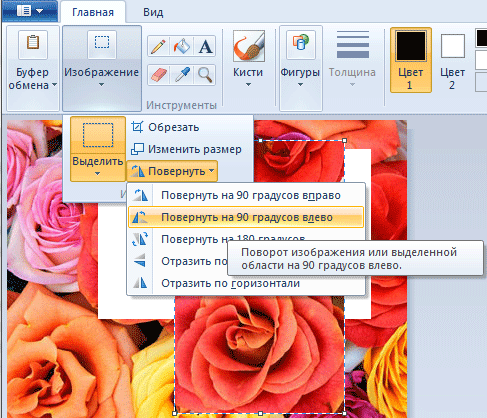
In addition, you can resize the selected fragment or crop the image, after which only the selected area will remain on the canvas, and the rest of the image will be deleted.
To accurately and conveniently create a drawing, you can use some additional elements of the Paint editor, which are located in the tab View.

Here you will find commands for changing the scale of the work area, rotating the image to full screen, as well as showing or hiding the thumbnail window. In Group Show or hide You can enable the display of rulers and grid lines on the canvas for easy alignment and determination of the size of objects in the image, as well as more accurate positioning of the mouse cursor. Here you can hide the status bar by unchecking the item of the same name.
We looked at some tools for creating images, as well as the procedure for saving drawn drawings to a file. But how can you open previously saved images for later editing? To open an image file, you need to click on the button Paint blue color with a triangle, which is located on Lente to the left of the tab home.

In the main menu of the program that opens, select the item Open. Next, a standard window will appear allowing you to open files stored on your disks. In this window, you need to find the folder in which the file with the picture is located, click on the file name and click the “Open” button.
If you decide to create a new drawing, click the command in the menu that appears Create, if you decide to save the picture under a different name, click on the line Save as. A standard window for saving files will appear, where you can specify a different name. By the way, using the same command you can convert graphic files from one format to another, for example, a PNG image to JPEG or GIF.

To do this, you need to open the source image in the editor, click on the Paint button and hover the mouse cursor over the command Save as. An auxiliary window will open in front of you with a list of main graphic formats. By clicking on any of them, you can resave the file in the version you need.
In addition to opening and saving an image, it can be printed out on paper using a printing device (printer or MFP), which must be connected to a computer. The commands that are responsible for setting up the printing of images are located in the submenu that appears when you hover the mouse cursor over the item Seal.

By clicking on a menu item Seal a window of the same name is called up, where you can select the printer, page range, number of copies and make other settings immediately before starting to print the image on paper.
Menu item Page settings calls up a dialog box in which you can configure printing parameters, for example, the size and orientation of the paper used, indents from the edges of the sheet, alignment of the picture to the edges, and so on. If you select portrait orientation, the sheet will be positioned vertically, and landscape orientation will be horizontal.

Before the drawing is printed on paper, you can see on the screen how it will look on the sheet. This can be done by clicking on the item Preview.

The drawing will appear in the main part of the window as it will be printed on paper. In this case, you can zoom out or zoom in on the image by clicking on the zoom buttons located on the ribbon. Here you will also find buttons for viewing the previous or next page, as well as going to the page settings window and printing the drawing. If you need to close the preview, just click on the button Close preview window located on the ribbon on the right.
After finishing working with the Paint editor, you need to click on the standard button designed to close the window (the cross in the upper right corner) or click Exit on the menu Paint. At the same time, if you try to close the editor window when the last changes made have not been saved, an additional window will open, with three options offering exit with saving the drawing (the “Save” button) or without saving (the “Do not Save” button), as well as returning to editing (the “Cancel” button).
Methodological development
for 1st year students of the Faculty of Pharmacy
for a practical lesson on the topic
"Paint Graphics Editor"
1. Scientific and methodological substantiation of the topic:
The standard graphic editor Paint is convenient to use for creating simple drawings and editing images in Windows environment and include them as OLE objects in other applications such as WordPad. Basic features of the Paint editor. The Paint editor has the ability to load, edit and write full-screen images to a file. Since the editor supports OLE technology, the resulting pictures can be copied to the clipboard, formatted as an object, and embedded in the texts of the WordPad editor and other Windows applications. In this case, the Paint editor can be both a server and a client for dynamic data exchange between different applications
2. Brief theory:
The standard graphics editor Paint is convenient to use for creating simple drawings and editing images in the Windows environment.
One valuable feature is undoing the results of recent operations. It is implemented by the Undo command in the Edit position of the Main Menu. Another very valuable command is the ability to view drawings in detail (with observation of each pixel). To do this, use the Scale command in the View position of the Main Menu. The View Picture command allows you to view a full-screen image.
Rice. 1. Paint graphic editor window
Paint program window. The Paint graphical editor can work with only one document at a time, so the document window is part of the program window, as shown in Fig. 1.
The main menu of the Paint editor contains the following items:
File - the same operations with files as in the WordPad editor (specifying a new file, loading a file, writing a file with the current and changed name, printing a file with a printer), supplemented with options: pave the working Windows table, to the center of the Windows desktop.
Editing - editing a file, working with the clipboard, undoing previous actions and repeating the results of a canceled action.
View - controls the display of a menu of tools and colors, the text attribute panel, as well as the status bar, controls the scale and overview of images.
Drawing - operations with selected images (rotate, invert, change attributes, clear, change drawing parameters).
Palette - setting options for the graphic editor (setting and recording a color palette).
Help - access help for the graphic editor.
Except standard elements(header and horizontal menu), the window has horizontal and vertical scroll bars, as well as four special areas:
Working field;
Toolbar;
Color palette;
Field additional parameters tools.
Working field. The central part of the Paint window is occupied by the working area - the area of the screen on which you draw a picture. The size of the picture may exceed the size of the working field - in this case, only a fragment of the image is always on the screen, and you can move around the picture field using standard stripes scroll. The size of the picture may be smaller than the working field - in this case there are no scroll bars, and the picture field is limited by a frame in the upper left part of the working field.
Toolbar. On the left side of the Paint window there is a toolbar, each of which is indicated by a small icon. As you already know, such an icon can represent not only the actual “tool”, but also some operation that is performed after selecting this “tool”.
To select a tool, just click on it with the mouse. The icon of the selected tool is highlighted in color. If you want to use, say, an eraser, just click on it - the eraser icon will be highlighted.
What happens after choosing a particular tool?
Curly scissors. The mouse pointer turns into scissors (or rather, into a knife), with which we can cut (select) a fragment of any shape from the picture.
Rectangular scissors. The mouse pointer turns into scissors, with which we can cut a rectangular fragment from the picture.
Aerosol can. The mouse pointer turns into a stream of “aerosol can”, exactly the same as some fans “worked” with, painting the slogan “Spartak is the champion!” in the entrances. By moving the mouse across the screen, we paint the surface with streams of dots in the color of the symbol, “strokes”, the density of which depends on the speed of the pointer, and the size - on the current line width (you will learn about color and width later).
Entering text. After selecting this tool, you must position the pointer at the insertion point of a line of text and click the mouse: a text cursor will appear, inviting you to enter characters.
Eraser. The mouse pointer turns into a square eraser. By moving it, we “erase” areas of the image or change the color of the symbol to the background color.
Filling. The mouse pointer turns into a “paint can.” If you place it inside a closed cavity and click the mouse, the cavity will be filled with the symbol's current color.
Brush. The mouse pointer turns into a "brush". Additionally, we can select the brush shape. Drawing with such a pointer is no different from drawing with a regular brush (or, if you prefer, a “pencil”).
Curved line. Selecting this tool gives us the opportunity to draw a straight line with the pointer, and then bend it into a bizarre arc.
Straight line. The pointer turns into a “pencil”. With this pencil we can draw straight lines at any angle to the vertical of the screen.
Hollow and painted geometric shapes. By selecting any of these tools, we get the opportunity to draw a hollow or colored shape with the mouse cursor: rectangle, square, ellipse, circle, polygon, etc.
Color palette. A palette is a set of colors that is located at the bottom of the Paint window. In some ways, it's similar to an artist's palette, but whereas an artist can only use one paint on a brush at any time, Paint allows you to work with two colors at once: a foreground color and a background color. Because the foreground color is drawn text characters, it is often called the character color or primary color.
On the left side of the color palette are two overlapping rectangles. The small rectangle (in the center of the large one) is colored with the current symbol color, and the large rectangle is colored with the current background color. After launch Paint color symbol - black, background color - white.
You can change these colors at any time. To select the current symbol color, left-click on any of the colors in the palette, and to select a background color, right-click on any of the colors.
How are these colors used to create a picture?
Text characters are entered using the symbol color, lines, arcs and contours of hollow figures (rectangle, ellipse, polygon) are drawn. A brush and an aerosol can work in the color of the symbol; the cavities of the rectangle, ellipse and polygon are painted with the same color; Fill paints any closed cavities with the color of the symbol.
The background color colors the outlines of text characters and the outlines of filled shapes (rectangle, ellipse, and polygon).
In addition, below we will look at how character and background colors are used when working with erasers (simple and colored).
Additional tool parameters field. When you select some tools, a table with alternatives appears in the lower left window of the panel, as shown in Fig. 2.
Rice. 2. Alternative options parameters of some instruments
The table (1) appears when you select the Free Selection, Selection, and Caption (Text Input) tools. You can specify one of two operating modes for this tool: an opaque background (top rectangle) or a transparent background. If an opaque background is selected, when moving the fragment completely covers the existing picture, i.e. the background of the fragment is used. If a transparent background is selected, the background color of the fragment is not used when moving, i.e. the background of the existing picture shows through the fragment. Likewise, choosing a background model affects how you type text over an image.
The table (2) appears when you select the Eraser/Color Eraser tool and allows you to specify the size of the eraser.
The panel (3) appears when you select the “Zoom” tool and allows you to specify the scale of image magnification (100%, 200%, 600%, 800%).
The panel (4) allows you to select the shape of the “Brush” tool, and the panel (5) allows you to select the size of the “stroke” of the “Spray” tool.
The scoreboard (6) determines the line width when working with the “Line” and “Curve” tools.
The board (7) allows you to choose one of three ways to draw any of four geometric shapes: rectangle, polygon, ellipse and “rounded” rectangle. By clicking on the top swatch in the board, you can draw a hollow shape with an outline in the symbol's color; The middle swatch allows you to draw a background-colored shape with an outline in the symbol color, and the bottom swatch allows you to draw a background-colored shape without an outline.
Saving and loading images. The image is saved in raster format files with the extension .BMP, JPG, GIF, TIFF and PNG. The operations of loading (opening) and saving these files are subject to the strict Windows standard (the Open..., Save and Save As... commands of the File menu item Paint).
Basics of graphics editing techniques in Paint. After starting the program, the Paint window opens on the screen. The main tool when working with images in Paint is the mouse. You most often use the keyboard only to enter text.
The functions of most tools are already familiar to you, and some of the subtleties of their use are easy to master with experience. Therefore, only those features of the editing technique in Paint that cannot be considered obvious are discussed below.
Let's list some features of working with tools in Paint (compared to the same tools in Paintbrush). We will review the panel line by line: from left to right and from top to bottom.
1. Instead of an eraser and a colored eraser, Paint uses one tool: if you hold down the left mouse button, you have a simple eraser at your disposal, and if you hold down the right mouse button, you have a colored eraser.
2. Fill works basically the same as a paint brush in Paintbrush, but when you right-click, the enclosed area is filled with the background color.
3. The Color Picker, which was missing from Paintbrush, allows you to copy the color of a selected area of an image to another area of the drawing. Select the tool, click on the object whose color you want to copy, and then paint with the new symbol color.
4. Using the “Scale” tool, you can enlarge the visible part of the image by 2, 6, 8 times.
5. The Pencil Tool Lets You Draw arbitrary figures in the color of the symbol with lines one pixel thick.
6. The Brush and Spray tools work basically the same as their respective Paintbrush tools. However, if you hold down the left mouse button while spraying, the spray will be in the symbol color, if the right mouse button is pressed, it will be sprayed in the background color.
7. To enter text:
Click on the Lettering tool;
Draw a text frame;
Click inside the frame and type your text.
The font, font size, and font style can be selected using the Text Attributes panel. This panel will appear on the screen after checking the “Text Attributes Panel” checkbox in the View menu item or in the context menu.
Additional features of the graphic editor. We will briefly describe the additional features of Paint, which you can easily master using the horizontal menu and toolbar.
1. To edit details (pixel by pixel), you can simply enlarge the visible part of the image using the View-Zoom command and enable the “Show grid” checkbox there. If you select the Show Thumbnail checkbox at the same time, the editable area will be displayed in a frame on the screen in full size. In addition, the image can be enlarged using the Zoom tool (2x, 6x, 8x).
2. In the Picture menu item there are commands Flip/Rotate... and Stretch/Tilt..., which work both with the selected fragment and with the entire picture. The first command allows you to flip the image (from left to right or top to bottom), as well as rotate it by an angle of 90, 180, 270 degrees. The second command allows you to change the proportions of the image: stretch it horizontally or vertically (the “stretching factor” is set in percentages) and (or) tilt it horizontally or vertically (the tilt is set in degrees).
3. When you paste the contents of the clipboard or a picture from another file into a picture, you don’t have to worry about the size of the pasted image: Paint won’t crop it, even if it doesn’t fit in the working area of the window.
4. In Paint, it is possible to clear a selected fragment of a picture (command Edit-Clear Selection). To clear the entire image (if there are no selected fragments), select the Picture-Clear command.
5. In the Paint editor, you can undo not one, but three sequentially performed operations.
Graphic editors are those designed for creating and editing images (drawings).
Paint is the simplest graphics editor. In terms of its capabilities, it does not meet modern requirements, but due to its simplicity and accessibility it remains necessary component operating system. Having understood the principles of managing this program, it is easier to master other, more powerful tools for working with graphics.
The program is launched using the Start Programs Accessories Paint command.
The controls of the Paint working window, in addition to the menu bar, include a toolbar, a tool settings palette, and a color palette (see Figure 1). The toolbar buttons are used to call drawing and graphic tools. In the settings palette, you can select the tool parameters (line thickness, print shape, method of filling the shape, etc.). The color palette elements are used to select the foreground color of the image (by left-clicking) and the background color (by right-clicking).
Setting the size of the work area. Before starting work, you should at least approximately set the size of the future drawing. Dimensions are specified in the Width and Height fields of the Attributes dialog box (Drawing Attributes).
The size in centimeters is specified in cases where the work is intended to be output to a printing device (printer) or to embed an image on a page with text document. In cases where the drawing is intended to be reproduced on the screen, Points (pixels) are chosen as the unit of measurement. So, for example, if a picture is being prepared for use as a desktop background, its dimensions should be taken equal to the screen resolution of the monitor (640x480; 800x600; 1024x768 pixels, etc.).
Preparing to create “transparent” drawings. The ability to create "transparent" drawings is one of the features of the Paint editor for the Windows operating system.
In the Attributes dialog box, you can assign a single color (for example, white) to be used as the "transparent" color. Color transparency means that if a given image is displayed on top of another image (background), then the lower image will be visible through the upper one at those points that have a color designated “transparent”. However, the transparency property is not always saved in the picture file, but only in cases where a graphic format is selected when saving. GIF. Drawings with a transparent background are widely used to create Web pages on the Internet and when creating electronic documents, for example, in multimedia publications.
Basic drawing and graphic tools. All tools except the Eraser paint with the primary color (selected by left-clicking on the paint palette). The eraser erases the image, replacing it with the background color (selected by right-clicking in the paint palette).
The Line tool is designed for drawing straight lines. The line thickness is selected in the settings palette. Lines are drawn by dragging the mouse. To make the line “strict” (vertical, horizontal or inclined at an angle of 45°), you should hold down the SHIFT key when drawing it.
The Pencil tool is designed for drawing arbitrary lines. The line thickness is selected in the settings palette.
The Curve tool is used to create smooth curved lines. The thickness is selected in the settings palette. The construction is carried out in three steps. First, draw a straight line using the drawing method, then click and drag to the side of the line to set the first and second radii of curvature.
The Brush Tool can be used to freely draw arbitrary curves, like the Pencil, but it is more often used for drawing using the typing method. First, select a brush shape in the settings palette, and then click the left mouse button to apply impressions to the drawing without dragging the mouse.
The Spray tool is used both for free drawing and for drawing using the stamping method. The shape of the spot is selected in the settings palette.
The Rectangle tool is used to draw rectangular shapes. Drawing is done by dragging the mouse. In the settings palette, you can select the method for filling the rectangle. There are three options: No Fill (only the frame is drawn), Fill with the Background Color, and Fill with the Foreground Color.
If you hold down the SHIFT key while creating a rectangle, you will form the correct shape. For a rectangle, the correct shape is a square.
The similar Rounded Rectangle tool works in the same way and produces a rectangle with rounded corners.
The Polygon tool is designed for drawing arbitrary polygons. Drawing is performed by a series of consecutive clicks and dragging. If the end point of a polygon coincides with the start point, then the polygon is considered closed. Closed shapes can be automatically filled with paint based on the fill option selected in the Options palette.
The Ellipse tool is used to draw ellipses and circles. A circle is a special case of a “regular” ellipse. It is obtained when drawing with the SHIFT key pressed.
The Fill tool is used to fill closed paths with a foreground or background color. Filling with the foreground color is done by clicking the left mouse button, and filling with the background color is done by clicking the right mouse button.
The Color Picker tool allows you to accurately select a primary or secondary color, not from the paint palette, but directly from the drawing. This is important when you need to ensure color consistency in different areas of the image. After selecting the tool, move the pointer over the area of the drawing with the desired color and click the mouse button. If you click the left button, the current color becomes the foreground color, and if you click the right button, it becomes the background color.
Area selection tools. Two tools are designed for working with selected areas: Selection and Free Selection. The Selection tool creates not an arbitrary, but a rectangular selection area. The selected area can be deleted using the DELETE key, copied to the clipboard (CTRL+C), cut to the clipboard (CTRL+X) and pasted from the clipboard (CTRL+V).
Scaling images. To accurately fine-tune a drawing, it is sometimes necessary to increase its scale. The maximum magnification is eightfold. To change the scale, use the View Scale command. The same can be done using the Scale tool; in this case, the scale value is selected in the settings palette.
In 8x magnification mode, you can overlay an auxiliary grid on the drawing (View Zoom Show grid). Each cell of this grid represents one enlarged image point. In this mode it is convenient to edit the image by individual points.
Transformation of images. Transformations are automatic changes in the shape, location or size of graphic objects. Paint doesn't have a lot of transformation tools, but it does have some. They can be found in the Picture menu.
The Picture Flip/Rotate command opens the Flip and Rotate dialog box, which contains controls for displaying the picture symmetrically about the vertical or horizontal axis of symmetry, as well as for rotating it by a fixed angle, a multiple of 90°.
The Drawing Stretch/Skew command opens the Stretch and Skew dialog box. Its controls allow you to stretch the design horizontally and vertically or tilt it along the horizontal or vertical axis. The stretch parameters are specified in percentages, and the tilt parameters are specified in angular degrees.
The Picture Invert Colors command acts as a toggle. When using this command, the color of each pixel in the image changes to the “opposite” color. In this case, we called “opposite” the color that complements the given color to white. Entering text. The Paint program is a graphic editor and is not intended for working with text.
Therefore, entering text in this program is the exception, not the rule. Avoid using small characters that look untidy. Consider Paint's text mode only as a tool for creating short and large headings.
To enter text, use the Caption tool. Having selected the tool, click on the picture approximately where the inscription should begin - an input field will open in the picture. Text is entered into this field from the keyboard. The size of the input field is changed by dragging the input area handles - small rectangular nodes located on the sides and corners of the input area. Having finished entering, call the text attributes panel (View Text attributes panel). Using the controls of this panel, you can select the font shape, style and size.
3. The purpose of students’ activities in class:
The student must know:
1. The concept of graphic information.
2. Types graphic image.
The student must be able to:
1. Work with a graphic editor.
2. Create a graphic image.
3. Edit and change the graphic image.
Theoretical part:
1. The concept of a graphic image Paint.
2. Basic elements of the Paint graphic editor window.
3. Creating and editing graphic images in Paint-t.
4. Features of the Paint graphic editor.
Practical part:
Using the graphic editor Paint, depict the structural unit “Pharmacy” in the form of a diagram
5. List of questions to check the level of knowledge:
1. The concept of graphic image.
2. Types of graphic images.
3. The concept of a graphic editor.
6. List of questions to check the final level of knowledge:
1. Paint graphic editor window.
2. Graphic editor palette.
3. Graphic editor tools.
4. Types of object selection in a graphic editor.
5. Changing and editing the picture.
6. Inserting text into a graphic editor and editing text.
7. Independent work of students:
Explore the capabilities of the Photochop graphics editor.
8. Chronograph of the training session:
1. Organizational moment – 5 min.
2. Current knowledge control – 30 min.
3. Analysis of the topic – 20 min.
4. Practical work- 30 min.
5. Summing up the lesson – 10 min.
9. List of educational literature for the lesson:
1. COMPUTER SCIENCE practical course for students of medical universities.”
Arunyants G.G., Stolbovsky D.N., Kalinkin A.Yu.




